Scientific hypothesis and rational pharmacological for the use of sacubitril/valsartan in cardiac damage caused by COVID-19
- PMID: 33460992
- PMCID: PMC7788318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2021.110486
Scientific hypothesis and rational pharmacological for the use of sacubitril/valsartan in cardiac damage caused by COVID-19
Abstract
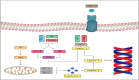
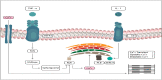
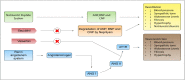
On March 11, 2020 the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the state of global pandemic caused by the new SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). To date, no antivirals directed against SARS-CoV-2 or effective vaccines to combat the viral infection are available. Severe acute respiratory syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2 is treated empirically with antivirals, anti-inflammatory, anticoagulants. The approval of an effective vaccine still takes time. In this state, it may be useful to find new therapeutic solutions from drugs already on the market. Recent hypotheses suggest that the use of AT-1 receptor antagonists (ARB) in combination with neprilisin inhibitors (NEPi) could indirectly provide clinical benefits to patients with SARS-CoV-2 and cardiac involvement. In this article we investigate and describe a possible innovative pharmacological approach for the treatment of the most severe stages of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: Cardiology; Covid-19; Cytokine; Neprilisin; Sacubitril; Sars-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the Authors have conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World health organization (WHO) https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel coronavirus2019/situation... (Situation Reports July 2020).
-
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus. 2020 Oct In: StatPearls [Internet]. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

