Adjuvant Pazopanib Versus Placebo After Nephrectomy in Patients With Localized or Locally Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Final Overall Survival Analysis of the Phase 3 PROTECT Trial
- PMID: 33461782
- PMCID: PMC8407394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.029
Adjuvant Pazopanib Versus Placebo After Nephrectomy in Patients With Localized or Locally Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Final Overall Survival Analysis of the Phase 3 PROTECT Trial
Abstract
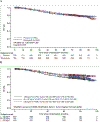
Most studies indicate no benefit of adjuvant therapy with VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). PROTECT (NCT01235962) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study to evaluate adjuvant pazopanib in patients with locally advanced RCC at high risk of relapse after nephrectomy (pazopanib, n = 769; placebo, n = 769). The results of the primary analysis showed no difference in disease-free survival between pazopanib 600 mg and placebo. Here we report the final overall survival (OS) analysis (median follow-up: pazopanib, 76 mo, interquartile range [IQR] 66-84; placebo, 77 mo, IQR 69-85). There was no significant difference in OS between the pazopanib and placebo arms (hazard ratio 1.0, 95% confidence interval 0.80-1.26; nominal p > 0.9). OS was worse for patients with T4 disease compared to those with less advanced disease and was better for patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 compared to those with lower BMI. OS was significantly better for patients who remained diseasefree at 2 yr after treatment compared with those who relapsed within 2 yr. These findings are consistent with the primary outcomes from PROTECT, indicating that adjuvant pazopanib does not confer a benefit in terms of OS for patients following resection of locally advanced RCC. PATIENT SUMMARY: In the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 PROTECT study, overall survival was similar for patients with locally advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) at high risk of relapse after nephrectomy who received adjuvant therapy with pazopanib or placebo. Pazopanib is not recommended as adjuvant therapy following resection of locally advanced RCC. This trial is registered at Clinicaltrials.gov as NCT01235962.
Keywords: Pazopanib; Renal cell carcinoma; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2020 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Re: Robert J. Motzer, Paul Russo, Naomi Haas, et al. Adjuvant Pazopanib Versus Placebo After Nephrectomy in Patients with Localized or Locally Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Final Overall Survival Analysis of the Phase 3 PROTECT Trial. Eur Urol 2021;79:334-8: PROTECTing Patients with Locally Advanced Kidney Cancer.Eur Urol. 2021 Jul;80(1):e33-e34. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.04.025. Epub 2021 May 4. Eur Urol. 2021. PMID: 33962807 No abstract available.
References
-
- Eisen TQG, Frangou E, Smith B, et al.Primary efficacy analysis results from the SORCE trial (RE05): adjuvant sorafenib for renal cell carcinoma at intermediate or high risk of relapse: an international, randomised double-blind phase III trial led by the MRC CTU at UCL. Ann Oncol 2019;30(Suppl 5):v851–934.
-
- Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, et al.Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. N Engl J Med 2016;375:2246–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

