Dichotic sentence identification test in Portuguese: a study in young adults
- PMID: 33461909
- PMCID: PMC9422703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.11.018
Dichotic sentence identification test in Portuguese: a study in young adults
Abstract
Introduction: Among the currently-applied auditory processing tests, dichotic listening tests have been widely used, since they allow investigating the hemispheric and inter-hemispheric function and their respective skills to process the received auditory information.
Objective: To obtain normality reference measures with the new dichotic sentence identification test in right-handed adults with normal hearing.
Methods: Quantitative, observational, cross-sectional study. 72 subjects were assessed, aged 19-44 years, right-handed, with normal hearing, without hearing complaints. The dichotic sentence identification test consists of different lists of sentences, which were combined two by two and presented at the same time, using earphones in both ears, at 50dB Sensation Level. The test was applied in four stages: training of the 3 stages, free attention, right and left directed attention, thus evaluating different auditory skills.
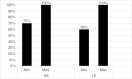
Results: In the free attention task, the average percentage of correct answers in the right ear was 93.59% and in the left ear 86.06%, with a statistically significant difference between the ears, with an advantage for the right ear. In the directed attention task, the average percentage of correct answers was 99.37% in the right ear and 98.8% in the left ear, with no statistical difference between the ears.
Conclusion: It is suggested, as a normality reference for the stage of free attention, 90%-100% for correct answers for the right ear and for the left ear, from 80% to 100%. When there is asymmetry between the ears, differences of up to 20% are expected, with an advantage for the right ear For the directed attention stage, the expected normality reference values are 100% for the right ear and for the left ear, with no asymmetry between the ears; however, if it occurs, a difference of 10% is expected between the ears, with an advantage for the right ear.
Keywords: Auditory perception; Hearing disorders; Hearing tests.
Copyright © 2020 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dichotic Sentences Test Performance of Adults with communication complaints.Codas. 2023 Aug 7;35(4):e20210301. doi: 10.1590/2317-1782/20232021301pt. eCollection 2023. Codas. 2023. PMID: 37556702 Free PMC article.
-
Verbal dichotic listening in developmental stuttering: subgroups with atypical auditory processing.Cogn Behav Neurol. 2004 Dec;17(4):224-32. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15622019 Clinical Trial.
-
Central auditory processing in aging: the dichotic listening paradigm.J Nutr Health Aging. 2010 Nov;14(9):751-6. doi: 10.1007/s12603-010-0097-7. J Nutr Health Aging. 2010. PMID: 21085905
-
How to get a left-ear advantage: A technical review of assessing brain asymmetry with dichotic listening.Scand J Psychol. 2018 Feb;59(1):66-73. doi: 10.1111/sjop.12408. Scand J Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29356005 Review.
-
"The Dichotic Digit Test" as an Index Indicator for Hearing Problem in Dementia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Acad Audiol. 2020 Oct;31(9):646-655. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1718700. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Am Acad Audiol. 2020. PMID: 33296935
Cited by
-
Dichotic Sentences Test Performance of Adults with communication complaints.Codas. 2023 Aug 7;35(4):e20210301. doi: 10.1590/2317-1782/20232021301pt. eCollection 2023. Codas. 2023. PMID: 37556702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Katz J., Wilde L. In: Handbook of clinical audiology. Katz J., editor. Williams & Wilkins; Baltimore: 1994. Auditory processing disorders; pp. 490–502.
-
- 2010. American Academy of Audiology Clinical Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Children and Adults With Central Auditory Processing Disorder [online]https://audiology-web.s3.amazonaws.com/migrated/CAPD%20Guidelines%208-20... Disponível em:
-
- Pereira L.D., Schochat E. Pro Fono; Barueri, São Paulo: 2011. Testes auditivos comportamentais para avaliação do processamento auditivo central.
-
- Chermak G.D., Musiek F.E. Volume 1. Plural Publishing; San Diego, CA: 2014. Auditory neuroscience and central auditory processing disorder; pp. 3–15. (Handbook of Central Auditory Processing Disorder: Auditory Neuroscience and Diagnosis).
-
- Neijenhuis K.A., Stollman M.H., Snik A.F., Van der Broek P. Development of a central auditory test battery for adults. Audiology. 2001;40:69–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

