The IL-6 antagonist tocilizumab is associated with worse depression and related symptoms in the medically ill
- PMID: 33462203
- PMCID: PMC7812704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-020-01164-y
The IL-6 antagonist tocilizumab is associated with worse depression and related symptoms in the medically ill
Abstract
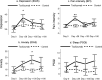
Because medical illness is associated with increased inflammation and an increased risk for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder, anti-cytokine therapy may represent a novel, and especially efficacious, treatment for depression. We hypothesized that blockade of the interleukin (IL)-6 signaling pathway with tocilizumab would decrease depression and related symptomatology in a longitudinal cohort of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) patients, a medically ill population with a significant inflammation and psychopathology. Patients undergoing allogeneic HCT received either a single dose of tocilizumab one day prior to HCT (n = 25), or HCT alone (n = 62). The primary outcome included depressive symptoms at 28 days post HCT; anxiety, fatigue, sleep, and pain were assessed at pretreatment baseline and days +28, +100, and +180 post HCT as secondary outcomes. Multivariate regression demonstrated that preemptive treatment with tocilizumab was associated with significantly higher depression scores at D28 vs. the comparison group (β = 5.74; 95% CI 0.75, 10.73; P = 0.03). Even after adjustment for baseline depressive symptoms, propensity score, and presence of acute graft-versus-host disease (grades II-IV) and other baseline covariates, the tocilizumab-exposed group continued to have significantly higher depression scores compared to the nonexposed group at D28 (β = 4.73; 95% CI 0.64, 8.81; P = 0.02). Despite evidence that IL-6 antagonism would be beneficial, blockade of the IL-6 receptor with tocilizumab among medically ill patients resulted in significantly more-not less-depressive symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of tocilizumab on patient reported outcomes and inflammatory biomarkers in hematopoietic cell transplantation.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 Jun 11;23:100480. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100480. eCollection 2022 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 35757656 Free PMC article.
-
Addition of interleukin-6 inhibition with tocilizumab to standard graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation: a phase 1/2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Dec;15(13):1451-1459. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71017-4. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25456364 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of pre-transplant depression on outcomes of allogeneic and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Cancer. 2017 May 15;123(10):1828-1838. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30546. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28102896 Free PMC article.
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
-
Tocilizumab in transplantation.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Jun;76(6):765-773. doi: 10.1007/s00228-020-02864-6. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32266480 Review.
Cited by
-
Depression, Anxiety, and Quality of Life in Patients Treated with Single Infusion Tocilizumab for COVID-19: A Follow-up, Controlled Study.Indian J Psychol Med. 2023 Jan;45(1):47-52. doi: 10.1177/02537176221140557. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Indian J Psychol Med. 2023. PMID: 36778618 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Anti-Interleukin-6 Agents on Psychopathology in a Sample of Patients with Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: An Observational Study.Brain Sci. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):47. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14010047. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38248262 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Inflammation in Depression and Beyond: A Primer for Clinicians.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024 Oct;26(10):514-529. doi: 10.1007/s11920-024-01526-z. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024. PMID: 39187612 Review.
-
Nonspecific Orbital Inflammation (NSOI): Unraveling the Molecular Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Modalities, and Therapeutic Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 26;25(3):1553. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031553. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating the Neuroimmunomodulation Frontier: Pioneering Approaches and Promising Horizons-A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 7;25(17):9695. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179695. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical