Distinct metabolic programs established in the thymus control effector functions of γδ T cell subsets in tumor microenvironments
- PMID: 33462452
- PMCID: PMC7610600
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-00848-3
Distinct metabolic programs established in the thymus control effector functions of γδ T cell subsets in tumor microenvironments
Abstract
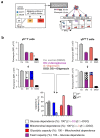
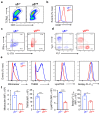
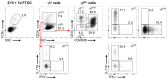
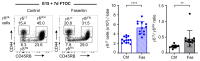
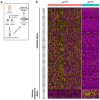
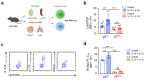
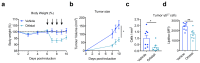
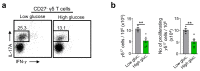
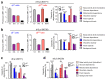
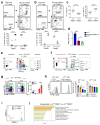
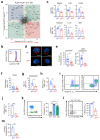
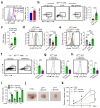
Metabolic programming controls immune cell lineages and functions, but little is known about γδ T cell metabolism. Here, we found that γδ T cell subsets making either interferon-γ (IFN-γ) or interleukin (IL)-17 have intrinsically distinct metabolic requirements. Whereas IFN-γ+ γδ T cells were almost exclusively dependent on glycolysis, IL-17+ γδ T cells strongly engaged oxidative metabolism, with increased mitochondrial mass and activity. These distinct metabolic signatures were surprisingly imprinted early during thymic development and were stably maintained in the periphery and within tumors. Moreover, pro-tumoral IL-17+ γδ T cells selectively showed high lipid uptake and intracellular lipid storage and were expanded in obesity and in tumors of obese mice. Conversely, glucose supplementation enhanced the antitumor functions of IFN-γ+ γδ T cells and reduced tumor growth upon adoptive transfer. These findings have important implications for the differentiation of effector γδ T cells and their manipulation in cancer immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
B.S.-S. is an inventor of the patented “Delta One T cell” technology, which has been acquired by GammaDelta Therapeutics (London, UK).
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 092973/Z/10/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG008155/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 646701/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- UH3 NS115064/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG062377/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- BB/R017808/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 1504814/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 092973/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- S10 OD020100/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI134861/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 NS115064/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

