Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition
- PMID: 33462485
- PMCID: PMC8515199
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-020-00763-1
Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition
Abstract
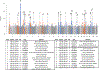
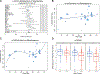
To study the effect of host genetics on gut microbiome composition, the MiBioGen consortium curated and analyzed genome-wide genotypes and 16S fecal microbiome data from 18,340 individuals (24 cohorts). Microbial composition showed high variability across cohorts: only 9 of 410 genera were detected in more than 95% of samples. A genome-wide association study of host genetic variation regarding microbial taxa identified 31 loci affecting the microbiome at a genome-wide significant (P < 5 × 10-8) threshold. One locus, the lactase (LCT) gene locus, reached study-wide significance (genome-wide association study signal: P = 1.28 × 10-20), and it showed an age-dependent association with Bifidobacterium abundance. Other associations were suggestive (1.95 × 10-10 < P < 5 × 10-8) but enriched for taxa showing high heritability and for genes expressed in the intestine and brain. A phenome-wide association study and Mendelian randomization identified enrichment of microbiome trait loci in the metabolic, nutrition and environment domains and suggested the microbiome might have causal effects in ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

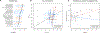

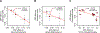
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 MH068457/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N01183X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RC2 MH089951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL127159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092127/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 19169/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 HG004729/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD011389/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65234/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- C18281/A19169/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- N01HC65235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS095775/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL140976/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N030125/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BRC-1215-20011/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/6/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002489/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204813/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 202802/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 29019/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

