A novel circulating miRNA-based signature for the early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 33463758
- PMCID: PMC7676218
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23505
A novel circulating miRNA-based signature for the early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a significant public health issue worldwide. The aim of our study was to develop a serum miRNA-based molecular signature for the early detection and prognosis prediction of NSCLC.
Methods: The significantly altered circulating miRNAs were profiled in GSE24709. The top ten upregulated miRNAs were miR-432, miR-942, miR-29c-5p, miR-601, miR-613, miR-520d-3p, miR-1261, miR-132-5p, miR-302b, and miR-154-5p, while the top ten downregulated miRNAs were miR-562, miR-18b, miR-9-3p, miR-154-3p, miR-20b, miR-18a, miR-487a, miR-20a, miR-103, and miR-144. Then, the top four upregulated serum miRNAs (miR-432, miR-942, miR-29c-5p, and miR-601) were validated by real-time quantitative PCR. The clinical significance of two candidate serum miRNAs, miR-942 and miR-601, was further explored.
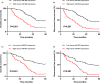
Results: Our results showed that the expression levels of serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 were significantly upregulated in NSCLC. In addition, serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 showed better performance than CEA, CYFRA21-1, and SCCA for early diagnosis of NSCLC. Combining serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 enhanced the efficacy of detecting early-stage NSCLC. Moreover, high serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 were both associated with adverse clinical variables and poor survival. The NSCLC patients with simultaneously high serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 suffered worst clinical outcome, while those with simultaneously low serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 had most favorable outcome. The multivariate analysis showed that serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 were independent prognostic factors for NSCLC.
Conclusions: Taken together, serum miR-942 and serum miR-601 might serve as a promising molecular signature for the early detection and prognosis prediction of NSCLC.
Keywords: early diagnosis; non–small‐cell lung cancer; prognosis prediction; serum miR‐601; serum miR‐942.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Detection of circulating exosomal miR-17-5p serves as a novel non-invasive diagnostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer patients.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Aug;215(8):152466. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152466. Epub 2019 May 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31146974
-
Circulating miRNA panels as a novel non-invasive diagnostic, prognostic, and potential predictive biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Br J Cancer. 2024 Nov;131(8):1350-1362. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02831-3. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39215192 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of serum miRNAs by nano-quantum dots microarray as diagnostic biomarkers for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7777-84. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4608-3. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26695145
-
Identification of differentially expressed circulating serum microRNA for the diagnosis and prognosis of Indian non-small cell lung cancer patients.Curr Probl Cancer. 2020 Aug;44(4):100540. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100540. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Curr Probl Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32007320 Review.
-
The role of MicroRNAs as early biomarkers of asbestos-related lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pulmonology. 2025 Dec 31;31(1):2416792. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2024.02.002. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Pulmonology. 2025. PMID: 38402124
Cited by
-
Serum Insights: Leveraging the Power of miRNA Profiling as an Early Diagnostic Tool for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;15(20):4910. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204910. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894277 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Selected miRNAs as Diagnostic, Predictive and Prognostic Markers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Pers Med. 2022 Jul 27;12(8):1227. doi: 10.3390/jpm12081227. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36013176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications in early stage lung cancer: pathogenesis, biomarkers, and early diagnosis.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 21;6(3):e70080. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70080. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39991629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual role of microRNA (miR)-20b in cancers: Friend or foe?Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jan 30;21(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01019-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36717861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal microRNAs in lung cancer: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):3090-3105. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2319. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988916 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7‐34. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Borghaei H, et al. Non‐small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2012;10(10):1236‐1271. - PubMed
-
- Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(1):39‐51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

