Clinicopathologic characteristics, pathology, and prognosis of 77 dogs with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 33463760
- PMCID: PMC7517845
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.15837
Clinicopathologic characteristics, pathology, and prognosis of 77 dogs with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a common cause of nonimmune complex glomerulopathy and the prognosis and clinicopathologic findings associated with this condition have not been described in dogs.
Objective: To characterize the presentation and identify clinical factors associated with the survival of dogs with FSGS.
Animals: Seventy-seven dogs diagnosed with FSGS based on evaluation of renal biopsy samples submitted to the International Veterinary Renal Pathology Service.
Methods: Retrospective review of medical records of dogs biopsied for evaluation of proteinuria between January 2015 and May 2017.
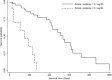
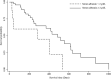
Results: The incidence of FSGS among all dogs biopsied for proteinuria was 26%. Significantly more females (48; 62.3%) than males (29; 37.7%) were affected (P = .04). At the time of biopsy, median serum creatinine concentration (SCr) was 1.2 mg/dL (range, 0.3-8.7), median serum albumin concentration (Alb) was 2.8 g/dL (range, 1.1-4.6), median systolic blood pressure was 153.5 mm Hg (range, 95-260), and median urine protein : creatinine ratio was 5.9 (range, 1.4-22). Median survival time after biopsy was 258 days (range, 26-1003) for dogs that died from all causes (n = 32). Factors that were associated with a shorter survival time included SCr ≥ 2.1 mg/dL (P < .01) and Alb < 2 g/dL (P < .01).
Conclusions and clinical importance: Most dogs with FSGS were female, and although commonly hypertensive, azotemia, severe hypoalbuminemia and ascites or edema were observed infrequently. Variables significantly associated with survival time were SCr and Alb.
Keywords: global glomerulosclerosis; glomerular disease; nonimmune complex glomerulopathy; podocyte; protein losing nephropathy; proteinuria; renal biopsy.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of survival among biopsy-determined categories of kidney disease in dogs.J Vet Intern Med. 2025 Mar-Apr;39(2):e17301. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17301. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39925194 Free PMC article.
-
European Veterinary Renal Pathology Service: A Survey Over a 7-Year Period (2008-2015).J Vet Intern Med. 2017 Sep;31(5):1459-1468. doi: 10.1111/jvim.14796. Epub 2017 Aug 1. J Vet Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28763127 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in Related Miniature Schnauzer Dogs.Vet Pathol. 2018 Mar;55(2):277-285. doi: 10.1177/0300985817736356. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Vet Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29191133
-
[Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after renal transplantation in a child with ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis: case report and literature review].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 2;54(12):936-940. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2016.12.013. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27938596 Review. Chinese.
-
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after renal transplantation.Clin Transplant. 2011 Jul;25 Suppl 23:6-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2011.01452.x. Clin Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21623907 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of survival among biopsy-determined categories of kidney disease in dogs.J Vet Intern Med. 2025 Mar-Apr;39(2):e17301. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17301. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39925194 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hypertension on the long-term prognosis of children with primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis-a retrospective cohort study.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):155-161. doi: 10.21037/tp-22-649. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36891366 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of proteinuria in dogs with telmisartan: A retrospective study.J Vet Intern Med. 2021 Jul;35(4):1810-1818. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16146. Epub 2021 May 10. J Vet Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33969924 Free PMC article.
-
A compared histopathological study on kidneys and eye bulbs in distinct clinical presentations of canine leishmaniasis by Leishmania infantum.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Aug;48(4):2243-2261. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10379-z. Epub 2024 May 8. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38717733
-
Urinary Electrophoretograms Performed by Capillary Electrophoresis: Comparison between Dogs and Cats.Gels. 2023 Jul 4;9(7):544. doi: 10.3390/gels9070544. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37504423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schneider SM, Cianciolo RE, Nabity MB, Clubb FJ Jr, Brown CA, Lees GE. Prevalence of immune‐complex glomerulonephritides in dogs biopsied for suspected glomerular disease: 501 cases (2007‐2012). J Vet Intern Med. 2013;27(suppl 1):S67‐S75. - PubMed
-
- Sim JJ, Batech M, Hever A, et al. Distribution of biopsy‐proven presumed primary glomerulonephropathies in 2000‐2011 among a racially and ethnically diverse US population. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;68:533‐544. - PubMed
-
- D'Agati VD, Kaskel FJ, Falk RJ. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2398‐2411. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

