Ghrelin, via corticotropin-releasing factor receptors, reduces glucose uptake and increases lipid content in mouse myoblasts cells
- PMID: 33463908
- PMCID: PMC7814488
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.14654
Ghrelin, via corticotropin-releasing factor receptors, reduces glucose uptake and increases lipid content in mouse myoblasts cells
Abstract
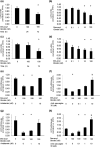
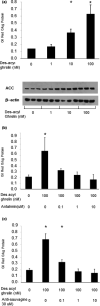
Ghrelin and the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) family are known regulators of cellular metabolism and energy balance. We previously demonstrated that myoblast glucose metabolism is regulated by ghrelin and that this effect is mediated by CRF receptor type 2 (CRF-R2). Here we explored the effect of des-acyl ghrelin, the major circulating isoform of ghrelin, on cellular metabolism in mouse myoblast C2C12 cells, and examined whether CRF family receptors mediate its metabolic effects in muscle cells. C2C12 cells were exposed to des-acyl ghrelin with or without the CRF-R1- and CRF-R2-specific antagonists antalarmin or antisauvagine-30, respectively. Des-acyl ghrelin reduced glucose uptake and expression of the glucose transporter GLUT4, but induced retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) expression. Antalarmin and antisauvagine-30 inhibited the induction of glucose uptake by des-acyl ghrelin and its effect on GLUT4 and RBP4 expression. Moreover, treating C2C12 cells with des-acyl ghrelin resulted in cAMP activation in response to the CRF-R1-specific ligand stressin, and the CRF-R2-specific ligand Ucn3. Furthermore, des-acyl ghrelin reduced the expression of uncoupling proteins UCP2 and UCP3. Adding antalarmin or antisauvagine-30 to the medium reversed this effect. Finally, des-acyl ghrelin elevated lipid content and acetyl-CoA carboxylase expression in C2C12 cells. Our results suggest that during food deprivation, des-acyl ghrelin signals the muscle cells that glucose levels are low and that they should switch to fatty acids for their metabolic fuel.
Keywords: C2C12 cell; CRF receptor; des-acyl ghrelin; glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism.
© 2021 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any potential conflicts of interest associated with this research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CRF type 2 receptors mediate the metabolic effects of ghrelin in C2C12 cells.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 Feb;22(2):380-9. doi: 10.1002/oby.20535. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 23804489 Free PMC article.
-
Des-acyl ghrelin acts by CRF type 2 receptors to disrupt fasted stomach motility in conscious rats.Gastroenterology. 2005 Jul;129(1):8-25. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.04.015. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 16012930
-
Intracerebroventricular urocortin 3 counteracts central acyl ghrelin-induced hyperphagic and gastroprokinetic effects via CRF receptor 2 in rats.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Oct 3;10:3281-3290. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S113195. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27757017 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and obestatin on the gastrointestinal motility.Peptides. 2011 Nov;32(11):2348-51. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.07.020. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 21835213 Review.
-
The ghrelin O-acyltransferase-ghrelin system: a novel regulator of glucose metabolism.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011 Feb;18(1):50-5. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e328341e1d3. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011. PMID: 21150588 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of diet and chronic exercise on skeletal muscle ghrelin response.Metabol Open. 2022 Mar 18;14:100182. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2022.100182. eCollection 2022 Jun. Metabol Open. 2022. PMID: 35340718 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin and LEAP2: Their Interaction Effect on Appetite Regulation and the Alterations in Their Levels Following Bariatric Surgery.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Aug 12;61(8):1452. doi: 10.3390/medicina61081452. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40870497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Des-acyl Ghrelin on Insulin Sensitivity and Macrophage Polarization in Adipose Tissue.J Transl Int Med. 2021 Jul 2;9(2):84-97. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2021-0025. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Transl Int Med. 2021. PMID: 34497748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asakawa, A. , Inui, A. , Kaga, T. , Yuzuriha, H. , Nagata, T. , Fujimiya, M. , Katsuura, G. , Makino, S. , Fujino, M. A. , & Kasuga, M. (2001). A role of ghrelin in neuroendocrine and behavioral responses to stress in mice. Neuroendocrinology, 74, 143–147. - PubMed
-
- Barazzoni, R. , Bosutti, A. , Stebel, M. , Cattin, M. R. , Roder, E. , Visintin, L. , Cattin, L. , Biolo, G. , Zanetti, M. , & Guarnieri, G. (2005). Ghrelin regulates mitochondrial‐lipid metabolism gene expression and tissue fat distribution in liver and skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism, 288, E228–E235. - PubMed
-
- Barazzoni, R. , Zanetti, M. , Cattin, M. R. , Visintin, L. , Vinci, P. , Cattin, L. , Stebel, M. , & Guarnieri, G. (2007). Ghrelin enhances in vivo skeletal muscle but not liver AKT signaling in rats. Obesity (Silver Spring), 15, 2614–2623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

