The emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in esophageal carcinoma: from underlying mechanisms to clinical implications
- PMID: 33464385
- PMCID: PMC11071794
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03751-0
The emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in esophageal carcinoma: from underlying mechanisms to clinical implications
Abstract
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), a type of transcriptional product more than 200 nucleotides in length, have emerged as crucial regulators in human cancers. Accumulating data have recently indicated relationships between lncRNAs and esophageal carcinoma (EC). Of note, lncRNAs act as decoys/sponges, scaffolds, guides, and signals to regulate the expression of oncogenes or tumor suppressors at epigenetic, post-transcriptional, and protein levels, through which they exert their unique EC-driving or EC-suppressive functions. Moreover, the features of EC-related lncRNAs have been gradually exploited for developing novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in clinical scenarios. LncRNAs have the potential to be used as diagnostic and prognostic indicators individually or in combination with other clinical variables. Beyond these, although the time is not yet ripe, therapeutically targeting EC-related lncRNAs via gene editing, antisense oligonucleotides, RNA interference, and small molecules is likely one of the most promising therapeutic strategies for the next generation of cancer treatment. Herein, we focus on summarizing EC-driving/suppressive lncRNAs, as well as discussing their different features regarding expression profiles, modes of action, and oncological effects. Moreover, we further discuss current challenges and future developing possibilities of capitalizing on lncRNAs for EC early diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Biomarker; Drug resistance; Early diagnosis; Esophageal cancer; Noncoding RNA; Targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
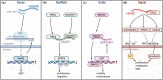
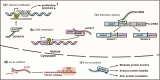
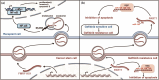
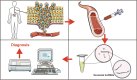
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Grant No. 81970481/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82000514/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 81602627/National Natural Science Foundation of China (CN)
- Grant No. 2018HH0150/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province
- Grant No. 2017GH00072/Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau Program (CN)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

