Noninvasive assessment of radiation-induced renal injury in mice
- PMID: 33464992
- PMCID: PMC8352084
- DOI: 10.1080/09553002.2021.1876950
Noninvasive assessment of radiation-induced renal injury in mice
Abstract
Purpose: The kidney is a radiosensitive late-responding normal tissue. Injury is characterized by radiation nephropathy and decline of glomerular filtration rate (GFR). The current study aimed to compare two rapid and cost-effective methodologies of assessing GFR against more conventional biomarker measurements.
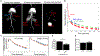
Methods: C57BL/6 mice were treated with bilateral focal X-irradiation (1x14Gy or 5x6Gy). Functional measurements of kidney injury were assessed 20 weeks post-treatment. GFR was estimated using a transcutaneous measurement of fluorescein-isothiocyanate conjugated (FITC)-sinistrin renal excretion and also dynamic contrast-enhanced CT imaging with a contrast agent (ISOVUE-300 Iopamidol).
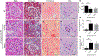
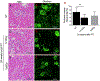
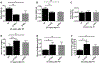
Results: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Periodic acid-Schiff staining identified comparable radiation-induced glomerular atrophy and mesangial matrix accumulation after both radiation schedules, respectively, although the fractionated regimen resulted in less diffuse tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Albumin-to-creatinine ratios (ACR) increased after irradiation (1x14Gy: 100.4 ± 12.2 µg/mg; 6x5Gy: 80.4 ± 3.02 µg/mg) and were double that of nontreated controls (44.9 ± 3.64 µg/mg). GFR defined by both techniques was negatively correlated with BUN, mesangial expansion score, and serum creatinine. The FITC-sinistrin transcutaneous method was more rapid and can be used to assess GFR in conscious animals, dynamic contrast-enhanced CT imaging technique was equally safe and effective.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that GFR measured by dynamic contrast-enhanced CT imaging is safe and effective compared to transcutaneous methodology to estimate kidney function.
Keywords: Radiobiology; irradiation; mouse; renal damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Alessia Fornoni is consultant for Hoffman-La Roche, Alexion, and Mesoblast on subject matters that are unrelated to this publication. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

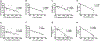
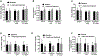
References
-
- Abboud I, Peraldi MN, Hingorani S. 2012. Chronic kidney diseases in long-term survivors after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: monitoring and management guidelines. Semin Hematol. 49(1):73–82. - PubMed
-
- Arveschoug AK, Kramer SM, Iversen P, Frokiaer J, Gronbaek H. 2015. Monitoring Kidney Function in Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients Treated with (90)Y-DOTATOC: Associations with Risk Factors. Curr Radiopharm. 8(1):49–55. - PubMed
-
- Brochner-Mortensen J 1985. Current status on assessment and measurement of glomerular filtration rate. Clin Physiol. 5(1):1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
