With or without internal limiting membrane peeling during idiopathic epiretinal membrane surgery: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 33465119
- PMCID: PMC7815136
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245459
With or without internal limiting membrane peeling during idiopathic epiretinal membrane surgery: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Although previously published meta-analyses have compared the surgical effects between the methods of Idiopathic epiretinal membrane (iERM) removal with or without ILM peeling, they did not reach an agreement.
Purpose: We aimed to provide more evidence for the treatment of iERM and whether additional ILM peeling was better or not by analyzing more updated studies and randomized control trials (RCTs).
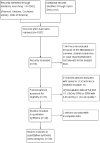
Method: The search was conducted in Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science and Open Grey without language limitation and the studies included were from inception to December 2019. All studies of iERM with or without ILM peeling showed at least one of outcomes, such as best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), central macular thickness (CMT) and recurrence of ERM. The pooled results between above groups were showed by the mean differences (MDs) and risk ratios (RR) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
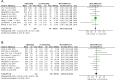
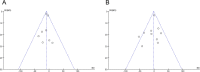
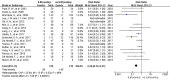
Result: In total, 1645 eyes of five randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and fifteen retrospective studies were included. The short-term (<12 months) BCVA improvement in both groups showed no significant difference (MD = -0.01; 95% CI = -0.02 to 0.01; P = 0.36). However, the BCVA improvement was significantly better in ILM peeling eyes than in those without ILM peeling when considering the risk bias (MD = -0.04; 95% CI = -0.07 to -0.01; P = 0.008). The short-term (<12 months) CMT had a higher reduction in non ILM peeling group (MD = -9.02; 95% CI = -12.51 to -5.54; P < 0.00001) and the recurrence of ERM in ILM peeling group was lower (P < 0.00001). The long-term (≥12months) BCVA improvement ((MD = -0.00; 95% CI = -0.03 to 0.03; P = 0.97) and reduction of long-term (≥12months) CMT (MD = -1.14; 95% CI = -7.14 to -4.86; P = 0.71) were similar in both groups.
Conclusion: By considering the risk of bias, we should determine whether ILM peeling is beneficial for short-term changes in BCVA in patients with iERM. Nevertheless, further studies are needed to confirm this. iERM removal without ILM peeling can improve the short-term decrease in CMT and ILM peeling decreases the recurrence of ERM, but the long-term changes in BCVA and CMT are similar with or without ILM peeling. There is a need for a true large scale randomized trial that will also include microperimetry and other functional measures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Bringmann A, Wiedemann P. Involvement of Muller glial cells in epiretinal membrane formation. Graefe's archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 2009;247(7):865–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

