T-bet-dependent ILC1- and NK cell-derived IFN-γ mediates cDC1-dependent host resistance against Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 33465134
- PMCID: PMC7875365
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008299
T-bet-dependent ILC1- and NK cell-derived IFN-γ mediates cDC1-dependent host resistance against Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
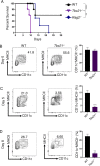
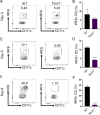
Host resistance against intracellular pathogens requires a rapid IFN-γ mediated immune response. We reveal that T-bet-dependent production of IFN-γ is essential for the maintenance of inflammatory DCs at the site of infection with a common protozoan parasite, Toxoplasma gondii. A detailed analysis of the cellular sources for T-bet-dependent IFN-γ identified that ILC1s and to a lesser degree NK, but not TH1 cells, were involved in the regulation of inflammatory DCs via IFN-γ. Mechanistically, we established that T-bet dependent innate IFN-γ is critical for the induction of IRF8, an essential transcription factor for cDC1s. Failure to upregulate IRF8 in DCs resulted in acute susceptibility to T. gondii infection. Our data identifies that T-bet dependent production of IFN-γ by ILC1 and NK cells is indispensable for host resistance against intracellular infection via maintaining IRF8+ inflammatory DCs at the site of infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Sullivan BM, Jobe O, Lazarevic V, Vasquez K, Bronson R, Glimcher LH, et al. Increased susceptibility of mice lacking T-bet to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis correlates with increased IL-10 and decreased IFN-gamma production. Journal of immunology. 2005;175(7):4593–602. Epub 2005/09/24. 10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4593 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- López-Yglesias AH, Burger E, Araujo A, Martin AT, Yarovinsky F. T-bet-independent Th1 response induces intestinal immunopathology during Toxoplasma gondii infection. Mucosal immunology. 2018. 10.1038/mi.2017.102 https://www.nature.com/articles/mi2017102#supplementary-information. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

