miR-34a in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduces rheumatoid arthritis inflammation via the cyclin I/ATM/ATR/p53 axis
- PMID: 33465281
- PMCID: PMC7882978
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15857
miR-34a in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduces rheumatoid arthritis inflammation via the cyclin I/ATM/ATR/p53 axis
Abstract
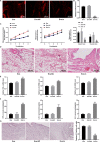
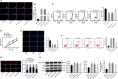
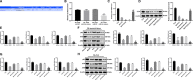
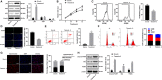
Extracellular vesicles (Evs) participate in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to determine the mechanism by which microRNA-34a (miR-34a) contained in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BM-MSC)-derived Evs functions in RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLSs). BM-MSC-derived Evs and an Evs inhibitor were extracted. A rat model of RA was established. miR-34a gain- and loss-of-function experiments were performed, and the inflammation in rat synovial fluid and tissues was detected. The role of miR-34a in RA-FLSs was also measured in vitro. The target gene of miR-34a was predicted using the online software TargetScan and identified using a dual-luciferase reporter gene assay, and the activation of the ATM/ATR/p53 signalling pathway was assessed. BM-MSC-derived Evs mainly elevated miR-34a expression, which reduced RA inflammation in vivo and inhibited RA-FLS proliferation and resistance to apoptosis in vitro, while inhibited miR-34a expression enhanced RA development. In addition, miR-34a could target cyclin I to activate the ATM/ATR/p53 signalling pathway, thus inhibiting abnormal RA-FLS growth and RA inflammation. Our study showed that miR-34a contained in BM-MSC-derived Evs could reduce RA inflammation by inhibiting the cyclin I/ATM/ATR/p53 signalling pathway.
Keywords: ATM/ATR/p53 signalling pathway; Cyclin I; MicroRNA-34a; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles: immunomodulation, diagnosis, and promising therapeutic roles for rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 18;15:1499929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1499929. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39624102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influences of the lncRNA TUG1-miRNA-34a-5p network on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis through targeting the lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA).J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Sep;35(9):e23969. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23969. Epub 2021 Aug 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34403518 Free PMC article.
-
RA Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Angiogenesis by miRNA-1972 Targeting p53/mTOR Signaling in Vascular Endotheliocyte.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 8;13:793855. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.793855. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35350778 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing long non-coding RNA NEAT1 attenuates rheumatoid arthritis via the MAPK/ERK signalling pathway by downregulating microRNA-129 and microRNA-204.RNA Biol. 2021 May;18(5):657-668. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1857941. Epub 2021 Jan 20. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33258403 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1912. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01912. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility and Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 24;13:838884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838884. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35401568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes as a Novel Anti-Inflammatory Agent and the Current Therapeutic Targets for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 18;10(7):1725. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071725. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: immunomodulation, diagnosis, and promising therapeutic roles for rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 18;15:1499929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1499929. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39624102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT2 promotes cardiac fibrosis following myocardial infarction and is regulated by miR-141.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):715. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10147. Epub 2021 May 3. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34007324 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the ferroptosis-related gene signature and the associated regulation axis in lung cancer and rheumatoid arthritis.Genes Immun. 2024 Oct;25(5):367-380. doi: 10.1038/s41435-024-00287-2. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Genes Immun. 2024. PMID: 39080453
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BK20181133/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- KJ2018A0814/Key Project in Natural Science Research in Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province
- KJ2019A1096/Key Project in Natural Science Research in Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province
- 2018SEYL008/Scientific Research Project of Anhui Provincial Health and Family Planning Commision
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

