A simple model of immune and muscle cell crosstalk during muscle regeneration
- PMID: 33465385
- PMCID: PMC8753861
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2021.108543
A simple model of immune and muscle cell crosstalk during muscle regeneration
Abstract
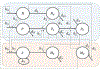
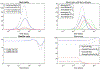
Muscle injury during aging predisposes skeletal muscles to increased damage due to reduced regenerative capacity. Some of the common causes of muscle injury are strains, while other causes are more complex muscle myopathies and other illnesses, and even excessive exercise can lead to muscle damage. We develop a new mathematical model based on ordinary differential equations of muscle regeneration. It includes the interactions between the immune system, healthy and damaged myonuclei as well as satellite cells. Our new mathematical model expands beyond previous ones by accounting for 21 specific parameters, including those parameters that deal with the interactions between the damaged and dead myonuclei, the immune system, and the satellite cells. An important assumption of our model is the replacement of only damaged parts of the muscle fibers and the dead myonuclei. We conduce systematic sensitivity analysis to determine which parameters have larger effects on the model and therefore are more influential for the muscle regeneration process. We propose additional validation for these parameters. We further demonstrate that these simulations are species-, muscle-, and age-dependent. In addition, the knowledge of these parameters and their interactions, may suggest targeting or selecting these interactions for treatments that accelerate the muscle regeneration process.
Keywords: Mathematical modeling; Muscle; Myotubes; Regeneration.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
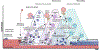
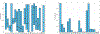
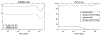
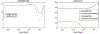
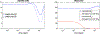
References
-
- Karalaki M, Fili S, Philippou A, Koutsilieris M, Muscle Regeneration: Cellular and Molecular Events, In Vivo 23 (5) (2009) 779–796. - PubMed
-
- Choi S-J, Age-related functional changes and susceptibility to eccentric contraction-induced damage in skeletal muscle cell, Integrative Medicine Research 5 (3) (2016) 171–175, special Issue - IMPACT (Integrative Medicine: Physical Activity is a Core Tip). doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2016.05.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

