Hydrogel microspheres for spatiotemporally controlled delivery of RNA and silencing gene expression within scaffold-free tissue engineered constructs
- PMID: 33465507
- PMCID: PMC7990721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.01.013
Hydrogel microspheres for spatiotemporally controlled delivery of RNA and silencing gene expression within scaffold-free tissue engineered constructs
Abstract
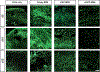
Delivery systems for controlled release of RNA interference (RNAi) molecules, including small interfering (siRNA) and microRNA (miRNA), have the potential to direct stem cell differentiation for regenerative musculoskeletal applications. To date, localized RNA delivery platforms in this area have focused predominantly on bulk scaffold-based approaches, which can interfere with cell-cell interactions important for recapitulating some native musculoskeletal developmental and healing processes in tissue regeneration strategies. In contrast, scaffold-free, high density human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC) aggregates may provide an avenue for creating a more biomimetic microenvironment. Here, photocrosslinkable dextran microspheres (MS) encapsulating siRNA-micelles were prepared via an aqueous emulsion method and incorporated within hMSC aggregates for localized and sustained delivery of bioactive siRNA. siRNA-micelles released from MS in a sustained fashion over the course of 28 days, and the released siRNA retained its ability to transfect cells for gene silencing. Incorporation of fluorescently labeled siRNA (siGLO)-laden MS within hMSC aggregates exhibited tunable siGLO delivery and uptake by stem cells. Incorporation of MS loaded with siRNA targeting green fluorescent protein (siGFP) within GFP-hMSC aggregates provided sustained presentation of siGFP within the constructs and prolonged GFP silencing for up to 15 days. This platform system enables sustained gene silencing within stem cell aggregates and thus shows great potential in tissue regeneration applications. STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE: This work presents a new strategy to deliver RNA-nanocomplexes from photocrosslinked dextran microspheres for tunable presentation of bioactive RNA. These microspheres were embedded within scaffold-free, human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC) aggregates for sustained gene silencing within three-dimensional cell constructs while maintaining cell viability. Unlike exogenous delivery of RNA within culture medium that suffers from diffusion limitations and potential need for repeated transfections, this strategy provides local and sustained RNA presentation from the microspheres to cells in the constructs. This system has the potential to inhibit translation of hMSC differentiation antagonists and drive hMSC differentiation toward desired specific lineages, and is an important step in the engineering of high-density stem cell systems with incorporated instructive genetic cues for application in tissue regeneration.
Keywords: Aggregates; Gene therapy; Mesenchymal stem cells; RNA interference; Sustained delivery.
Copyright © 2021 Acta Materialia Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

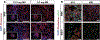
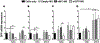
Similar articles
-
RNA interfering molecule delivery from in situ forming biodegradable hydrogels for enhancement of bone formation in rat calvarial bone defects.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jul 15;75:105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29885529 Free PMC article.
-
A microparticle approach for non-viral gene delivery within 3D human mesenchymal stromal cell aggregates.Acta Biomater. 2019 Sep 1;95:408-417. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.04.038. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31004846 Free PMC article.
-
Acceleration of chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by sustained growth factor release in 3D graphene oxide incorporated hydrogels.Acta Biomater. 2020 Mar 15;105:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.01.048. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32035282
-
Green fluorescent protein specified small interfering RNA-cross-linked iron oxide nanoparticles-Cy5.5.2008 Apr 17 [updated 2008 May 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Apr 17 [updated 2008 May 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641481 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Engineered Hydrogels for Local and Sustained Delivery of RNA-Interference Therapies.Adv Healthc Mater. 2017 Jan;6(1):10.1002/adhm.201601041. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601041. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. PMID: 27976524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tailoring biomaterials for vaccine delivery.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 12;22(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02758-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39135073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Progress of RNA-Based Antitumor Therapeutics.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;19(10):3159-3183. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.83732. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37416764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions Between Immunomodulatory Biomaterials and Immune Microenvironment: Cues for Immunomodulation Strategies in Tissue Repair.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 May 13;10:820940. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.820940. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35646833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in the Field of Protein-Based Hydrogels: Main Types, Characteristics, and Their Applications.Gels. 2025 Apr 22;11(5):306. doi: 10.3390/gels11050306. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40422326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bioprinting in Otolaryngology: A Review.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Jul;12(19):e2203268. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202203268. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 36921327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raisin S, Belamie E, Morille M Non-viral gene activated matrices for mesenchymal stem cells based tissue engineering of bone and cartilage, Biomaterials 104 (2016) 223–37. - PubMed
-
- Hong E, Reddi AH MicroRNAs in chondrogenesis, articular cartilage, and osteoarthritis: implications for tissue engineering, Tissue Eng Part B Rev 18 (6) (2012) 445–53. - PubMed
-
- Bobick BE, Matsche AI, Chen FH, Tuan RS The ERK5 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways play opposing regulatory roles during chondrogenesis of adult human bone marrow-derived multipotent progenitor cells, J Cell Physiol 224 (1) (2010) 178–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

