Limbus-centered marking technique-assisted continuous circular capsulorhexis
- PMID: 33466181
- PMCID: PMC7808535
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024109
Limbus-centered marking technique-assisted continuous circular capsulorhexis
Abstract
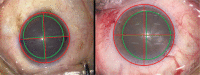
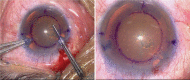
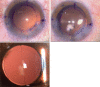
To introduce a limbus-centered continuous circular capsulorhexis (CCC) marking technique.Compared with traditional capsulotomy diameter mark technique, a self-designed limbus-centered capsulotomy mark (LCM) was used to perform the routine cataract surgery in this observational study. Ten eyes were included in each group. The area outer/inner 5.5-mm CCC ring, the furthest/nearest distance from the capsule margin to the intraocular lens (IOL) margin, the CCC total coverage IOL area were measured and compared between this 2 groups.No significant differences were found for all the comparison parameters between the 2 groups (all P > .05). However, the capsule total coverage area, area inner 5.5-mm ring was lower in the LCM group, which demonstrated advantage of LCM.The limbus-centered capsulotomy diameter mark, as an inexpensive and convenient method, helps to perform limbus-centered capsulorhexis with not only a 360° overlapping capsular edge but also well-centered IOL optics.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Posterior capsulorhexis combined with optic buttonholing: an alternative to standard in-the-bag implantation of sharp-edged intraocular lenses? A critical analysis of 1000 consecutive cases.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008 Jun;246(6):787-801. doi: 10.1007/s00417-008-0779-6. Epub 2008 Apr 19. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18425525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capsulotomy diameter mark.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003 Oct;29(10):1866-8. doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(03)00354-7. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003. PMID: 14604703
-
Comparison of postoperative axial stability of intraocular lens and capsulotomy parameters between precision pulse capsulotomy and continuous curvilinear capsulotomy: A prospective cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Nov;98(48):e18224. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018224. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31770285 Free PMC article.
-
[Preliminary report on the application of femtosecond laser-assisted anterior capsulotomy in intumescent white cataract surgery].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Apr 11;53(4):281-287. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2017.04.010. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28412801 Chinese.
-
Techniques of anterior capsulotomy in cataract surgery.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019 Apr;67(4):450-460. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1728_18. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30900573 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ridge operator-assisted delineation of capsulorhexis border for cataract surgery.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Aug 1;13(8):5119-5129. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-1319. Epub 2023 May 25. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37581076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith SR, et al. . The effect of lens edge design versus anterior capsule overlap on posterior capsule opacification. Am J Ophthalmol 2004;138:521–6. - PubMed
-
- Wallace RB, 3rd. Capsulotomy diameter mark. J Cataract Refract Surg 2003;29:1866–8. - PubMed
-
- Sacu S, et al. . Effect of intraocular lens optic edge design and material on fibrotic capsule opacification and capsulorhexis contraction. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004;30:1875–82. - PubMed
-
- Kellen RI. Capsulotomy diameter mark. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004;30:2031–2. - PubMed
-
- Camellin M, Gambino F, Casaro S. Measurement of the spatial shift of the pupil center. J Cataract Refract Surg 2005;31:1719–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

