Global Burden, Risk Factors, and Trends of Esophageal Cancer: An Analysis of Cancer Registries from 48 Countries
- PMID: 33466239
- PMCID: PMC7795486
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13010141
Global Burden, Risk Factors, and Trends of Esophageal Cancer: An Analysis of Cancer Registries from 48 Countries
Abstract
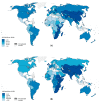
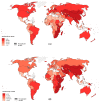
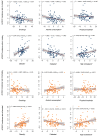
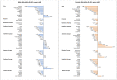
This study aimed to examine the global burden, risk factors, and trends of esophageal cancer based on age, sex, and histological subtype. The data were retrieved from cancer registries database from 48 countries in the period 1980-2017. Temporal patterns of incidence and mortality were evaluated by average annual percent change (AAPC) using joinpoint regression. Associations with risk factors were examined by linear regression. The highest incidence of esophageal cancer was observed in Eastern Asia. The highest incidence of adenocarcinoma (AC) was found in the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Ireland. A higher AC/squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) incidence ratio was associated with a higher prevalence of obesity and elevated cholesterol. We observed an incidence increase (including AC and SCC) in some countries, with the Czech Republic (female: AAPC 4.66), Spain (female: 3.41), Norway (male: 3.10), Japan (female: 2.18), Thailand (male: 2.17), the Netherlands (male: 2.11; female: 1.88), and Canada (male: 1.51) showing the most significant increase. Countries with increasing mortality included Thailand (male: 5.24), Austria (female: 3.67), Latvia (male: 2.33), and Portugal (male: 1.12). Although the incidence of esophageal cancer showed an overall decreasing trend, an increasing trend was observed in some countries with high AC/SCC incidence ratios. More preventive measures are needed for these countries.
Keywords: esophageal cancer; histological subtypes; incidence; mortality; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American Cancer Society Survival Rates for Esophageal Cancer. [(accessed on 10 June 2020)];2020 Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/esophagus-cancer/detection-diagnosis-stagi....
-
- Shapiro J., van Lanschot J.J.B., Hulshof M., van Hagen P., van Berge Henegouwen M.I., Wijnhoven B.P.L., van Laarhoven H.W.M., Nieuwenhuijzen G.A.P., Hospers G.A.P., Bonenkamp J.J., et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): Long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1090–1098. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00040-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Batran S.E., Homann N., Pauligk C., Goetze T.O., Meiler J., Kasper S., Kopp H.G., Mayer F., Haag G.M., Luley K., et al. Perioperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel versus fluorouracil or capecitabine plus cisplatin and epirubicin for locally advanced, resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FLOT4): A randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393:1948–1957. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32557-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wong M.C.S., Hamilton W., Whiteman D.C., Jiang J.Y., Qiao Y., Fung F.D.H., Wang H.H.X., Chiu P.W.Y., Ng E.K.W., Wu J.C.Y., et al. Global Incidence and mortality of oesophageal cancer and their correlation with socioeconomic indicators temporal patterns and trends in 41 countries. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:4522. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19819-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

