Cytochrome P450 CYP2E1 Suppression Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 33466250
- PMCID: PMC7824747
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10010052
Cytochrome P450 CYP2E1 Suppression Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
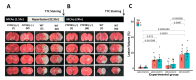
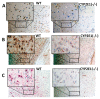
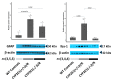
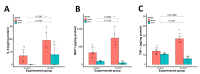
Despite existing strong evidence on oxidative markers overproduction following ischemia/reperfusion (I/R), the mechanism by which oxidative enzyme Cytochrome P450-2E1 (CYP2E1) contributes to I/R outcomes is not clear. In this study, we sought to evaluate the functional significance of CYP2E1 in I/R. CYP2E1 KO mice and controls were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo-90 min) followed by 24 h of reperfusion to induce focal I/R injury as an acute stage model. Then, histological and chemical analyses were conducted to investigate the role of CYP2E1 in lesion volume, oxidative stress, and inflammation exacerbation. Furthermore, the role of CYP2E1 on the blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity was investigated by measuring 20-hydroxyecosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) activity, as well as, in vivo BBB transfer rate. Following I/R, the CYP2E1 KO mice exhibited a significantly lower lesion volume, and neurological deficits compared to controls (p < 0.005). Moreover, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, apoptosis, and neurodegeneration were significantly lower in the CYP2E1(-/-) I/R group (p < 0.001). The BBB damage was significantly lower in CYP2E1(-/-) mice compared to wild-type (WT) (p < 0.001), while 20-HETE production was increased by 41%. Besides, inflammatory cytokines expression and the number of activated microglia were significantly lower in CYP2E1(-/-) mice following I/R. CYP2E1 suppression ameliorates I/R injury and protects BBB integrity by reducing both oxidative stress and inflammation.
Keywords: CYP2E1; blood-brain barrier; inflammation; ischemia/reperfusion; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The protective effect of HET0016 on brain edema and blood-brain barrier dysfunction after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.Brain Res. 2014 Jan 28;1544:45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.11.031. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24316243
-
Hyperlipidemia exacerbates cerebral injury through oxidative stress, inflammation and neuronal apoptosis in MCAO/reperfusion rats.Exp Brain Res. 2015 Oct;233(10):2753-65. doi: 10.1007/s00221-015-4269-x. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Exp Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26238404
-
NOD2 is involved in the inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and triggers NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Mar 25;11(5):525-35. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.10927. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25892960 Free PMC article.
-
Cepharanthine attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing NLRP3 inflammasome-induced inflammation and oxidative stress via inhibiting 12/15-LOX signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jul;127:110151. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110151. Epub 2020 May 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32559840
-
Overexpression of HSPA12B protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1832(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.10.003. Epub 2012 Oct 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23046810
Cited by
-
The Molecular Mechanisms of Ferroptosis and Its Role in Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 19;16:889765. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.889765. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35663422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Atlas of the Quantitative Protein Expression of Anti-Epileptic-Drug Transporters, Metabolizing Enzymes and Tight Junctions at the Blood-Brain Barrier in Epileptic Patients.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 9;13(12):2122. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122122. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959403 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and Characterization of CYP2E1-Overexpressing HepG2 Cells to Study the Role of CYP2E1 in Hepatic Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 1;24(9):8121. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098121. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175827 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Role of Sirtuin 1 in Cerebral Ischemia.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jul;43(5):1769-1783. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01288-3. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36153473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of unburned tobacco smoke on inflammatory and oxidative mediators in the rat prefrontal cortex.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 25;15:1328917. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1328917. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38333013 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

