Intake of Lactobacillus delbrueckii (pExu: hsp65) Prevents the Inflammation and the Disorganization of the Intestinal Mucosa in a Mouse Model of Mucositis
- PMID: 33466324
- PMCID: PMC7824804
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9010107
Intake of Lactobacillus delbrueckii (pExu: hsp65) Prevents the Inflammation and the Disorganization of the Intestinal Mucosa in a Mouse Model of Mucositis
Abstract
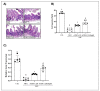
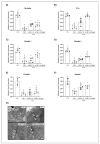
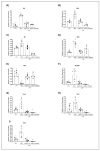
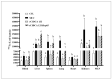
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is an antineoplastic drug that causes, as a side effect, intestinal mucositis, acute inflammation in the small bowel. The Heat Shock Protein (Hsp) are highly expressed in inflammatory conditions, developing an important role in immune modulation. Thus, they are potential candidates for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. In the mucositis mouse model, the present study aimed to evaluate the beneficial effect of oral administration of milk fermented by Lactobacillus delbrueckii CIDCA 133 (pExu:hsp65), a recombinant strain. This approach showed increased levels of sIgA in the intestinal fluid, reducing inflammatory infiltrate and intestinal permeability. Additionally, the histological score was improved. Protection was associated with a reduction in the gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as Tnf, Il6, Il12, and Il1b, and an increase in Il10, Muc2, and claudin 1 (Cldn1) and 2 (Cldn2) gene expression in ileum tissue. These findings are corroborated with the increased number of goblet cells, the electronic microscopy images, and the reduction of intestinal permeability. The administration of milk fermented by this recombinant probiotic strain was also able to reverse the high levels of gene expression of Tlrs caused by the 5-FU. Thus, the rCIDCA 133:Hsp65 strain was revealed to be a promising preventive strategy for small bowel inflammation.
Keywords: DNA delivery; bacterial translocation; gene expression; inflammation; intestinal mucositis; recombinant probiotics; technetium-99m.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lactobacillus delbrueckii CIDCA 133 Ameliorates Chemotherapy-Induced Mucositis by Modulating Epithelial Barrier and TLR2/4/Myd88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 26;13:858036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.858036. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35558121 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 11 delivered by dairy Lactococcus lactis strains modulates inflammation and prevents mucosal damage in a mice model of intestinal mucositis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1157544. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1157544. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37138633 Free PMC article.
-
Paraprobiotics and Postbiotics of Lactobacillus delbrueckii CIDCA 133 Mitigate 5-FU-Induced Intestinal Inflammation.Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 14;10(7):1418. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071418. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889136 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic synbiotic containing fructooligosaccharides and Lactobacillus delbrueckii CIDCA 133 alleviates chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis in mice.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 27;39(9):235. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03679-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37365380
-
Evidence supporting the use of probiotics for the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2011 Mar;51(3):239-47. doi: 10.1080/10408390903551747. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21390944 Review.
Cited by
-
The preventive effect of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum X86 isolated from raw milk on Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in rats.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 10;12:1476232. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1476232. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40129572 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulation of Polygonum bistorta root phenolic compounds as a novel phytobiotic and its protective effects in the mouse model of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Feb 15;23(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03868-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36793082 Free PMC article.
-
Anticandidal Activities by Lactobacillus Species: An Update on Mechanisms of Action.Front Oral Health. 2021 Jul 16;2:689382. doi: 10.3389/froh.2021.689382. eCollection 2021. Front Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 35048033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus delbrueckii CIDCA 133 Ameliorates Chemotherapy-Induced Mucositis by Modulating Epithelial Barrier and TLR2/4/Myd88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 26;13:858036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.858036. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35558121 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 11 delivered by dairy Lactococcus lactis strains modulates inflammation and prevents mucosal damage in a mice model of intestinal mucositis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1157544. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1157544. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37138633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gifoni M., Lima R.C., Lima A.A.M., Facanha A., Callado R.B., Azevedo C., De Albuquerque Ribeiro R. Clinical mucositis and intestinal permeability abnormalities in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan and 5-fluoruracil. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:e14183. doi: 10.1200/jco.2012.30.15_suppl.e14183. - DOI
-
- Chang C.-T., Ho T.-Y., Lin H., Liang J.-A., Huang H.-C., Li C.-C., Lo H.-Y., Wu S.-L., Huang Y.-F., Hsiang C.-Y. 5-Fluorouracil Induced Intestinal Mucositis via Nuclear Factor-κB Activation by Transcriptomic Analysis and In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e31808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031808. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Posner M.R., Haddad R.I. Novel agents for the treatment of mucositis. J. Support. Oncol. 2007;5:33–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

