Biological Nanopores: Engineering on Demand
- PMID: 33466427
- PMCID: PMC7824896
- DOI: 10.3390/life11010027
Biological Nanopores: Engineering on Demand
Abstract
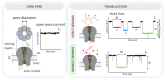
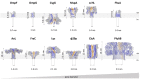
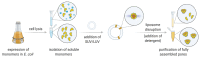
Nanopore-based sensing is a powerful technique for the detection of diverse organic and inorganic molecules, long-read sequencing of nucleic acids, and single-molecule analyses of enzymatic reactions. Selected from natural sources, protein-based nanopores enable rapid, label-free detection of analytes. Furthermore, these proteins are easy to produce, form pores with defined sizes, and can be easily manipulated with standard molecular biology techniques. The range of possible analytes can be extended by using externally added adapter molecules. Here, we provide an overview of current nanopore applications with a focus on engineering strategies and solutions.
Keywords: aptamers; nanopores; oligomerization; pore-forming toxins; sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
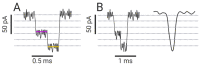





Similar articles
-
Biological nanopores for sensing applications.Proteins. 2022 Oct;90(10):1786-1799. doi: 10.1002/prot.26308. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Proteins. 2022. PMID: 35092317 Review.
-
Recent advances of small molecule detection in nanopore sensing.Talanta. 2024 Sep 1;277:126323. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126323. Epub 2024 May 25. Talanta. 2024. PMID: 38810384 Review.
-
Biological Nanopores: Confined Spaces for Electrochemical Single-Molecule Analysis.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Feb 20;51(2):331-341. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00143. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29364650
-
Nanoscale Probing of Informational Polymers with Nanopores. Applications to Amyloidogenic Fragments, Peptides, and DNA-PNA Hybrids.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Jan 15;52(1):267-276. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00565. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 30605305
-
Protein nanopore-based sensors for public health analyte detection.J Mater Chem B. 2024 Oct 9;12(39):9845-9862. doi: 10.1039/d4tb01149j. J Mater Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39258387 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytolysin A (ClyA): A Bacterial Virulence Factor with Potential Applications in Nanopore Technology, Vaccine Development, and Tumor Therapy.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jan 21;14(2):78. doi: 10.3390/toxins14020078. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35202106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State-of-the-art in engineering small molecule biosensors and their applications in metabolic engineering.SLAS Technol. 2024 Apr;29(2):100113. doi: 10.1016/j.slast.2023.10.005. Epub 2023 Oct 31. SLAS Technol. 2024. PMID: 37918525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Optical Spectroscopy for Multiplexed DNA and Protein-Sequencing with Plasmonic Nanopores: Challenges and Prospects.Anal Chem. 2022 Jan 18;94(2):503-514. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04459. Epub 2022 Jan 1. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 34974704 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Hitchhiker's Guide to Supplying Enzymatic Reducing Power into Synthetic Cells.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Apr 21;12(4):947-962. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00070. Epub 2023 Apr 13. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 37052416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic α-Helical Nanopore Reactor for Chemical Sensing.JACS Au. 2023 Aug 23;3(9):2467-2477. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00221. eCollection 2023 Sep 25. JACS Au. 2023. PMID: 37772177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Graham M. The Coulter principle: Foundation of an industry. J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2003;8:72–81. doi: 10.1016/S1535-5535-03-00023-6. - DOI
-
- DeBlois R.W., Bean C.P. Counting and sizing of submicron particles by the resistive pulse technique. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1970;41:909–916. doi: 10.1063/1.1684724. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

