Potential of Cucurbitacin B and Epigallocatechin Gallate as Biopesticides against Aphis gossypii
- PMID: 33466501
- PMCID: PMC7824822
- DOI: 10.3390/insects12010032
Potential of Cucurbitacin B and Epigallocatechin Gallate as Biopesticides against Aphis gossypii
Abstract
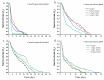
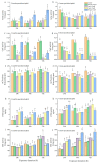
Aphis gossypii (Glover) is distributed worldwide and causes substantial economic and ecological problems owing to its rapid reproduction and high pesticide resistance. Plant-derived cucurbitacin B (CucB) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) are known to have insecticidal and repellent activities. However, their insecticidal activity on cotton- and cucurbit-specialized aphids (CO and CU), the two important host biotypes of A. gossypii, remains to be investigated. In the present study, we characterized, for the first time, the effects of these two plant extracts on the two host biotypes of A. gossypii. CucB and EGCG significantly reduced the A. gossypii population-level fitness and affected their ability to adapt to nonhost plants. Activities of important detoxification enzymes were also altered, indicating that pesticide resistance is weakened in the tested aphids. Our results suggest that CucB and EGCG have unique properties and may be developed as potential biopesticides for aphid control in agriculture.
Keywords: detoxification enzymes; nonhost adaptation; plant-derived pesticide; population-level fitness; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest for the current study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aphid adaptation to cucurbits: sugars, cucurbitacin and phloem structure in resistant and susceptible melons.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 May 5;23(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04248-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37147560 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of Cytochrome P450 Gene AgoCYP6CY19 Reduces the Tolerance to Host Plant in Cotton- and Cucumber-Specialized Aphids, Aphis gossypii.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Oct 5;70(39):12408-12417. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c05403. Epub 2022 Sep 26. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 36154024
-
Identification of Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Biotypes from Different Host Plants in North China.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 6;11(1):e0146345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146345. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26735973 Free PMC article.
-
An example of host plant expansion of host-specialized Aphis gossypii Glover in the field.PLoS One. 2017 May 17;12(5):e0177981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177981. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28545139 Free PMC article.
-
Vat, an Amazing Gene Conferring Resistance to Aphids and Viruses They Carry: From Molecular Structure to Field Effects.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Sep 26;7:1420. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01420. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27725823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aphid adaptation to cucurbits: sugars, cucurbitacin and phloem structure in resistant and susceptible melons.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 May 5;23(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04248-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37147560 Free PMC article.
-
Compatibility of Beauveria bassiana and a Plant Secondary Metabolite: A Novel Modeling Approach to Invade Host Defense for Effective Control of Oligonychus afrasiaticus (McGregor) on Date Palms.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;7(5):334. doi: 10.3390/jof7050334. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33926109 Free PMC article.
-
Topical RNA Interference Induces Mortality in the Cotton-Melon Aphid Aphis gossypii with No Adverse Effect on the Predator Propylea japonica.Insects. 2025 Mar 5;16(3):276. doi: 10.3390/insects16030276. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40266739 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids as Insecticides in Crop Protection-A Review of Current Research and Future Prospects.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 8;13(6):776. doi: 10.3390/plants13060776. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38592833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aphid-Resistant Plant Secondary Metabolites: Types, Insecticidal Mechanisms, and Prospects for Utilization.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 21;13(16):2332. doi: 10.3390/plants13162332. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blackman R., Eastop V.F. Aphids on The World’s Trees—An Identification and Information Guide. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; London, UK: 2000.
-
- Carvalho F. Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017;6:48–60. doi: 10.1002/fes3.108. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

