Lab-on-Microsphere-FRET-Based Multiplex Sensor Platform
- PMID: 33466522
- PMCID: PMC7824841
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11010109
Lab-on-Microsphere-FRET-Based Multiplex Sensor Platform
Abstract
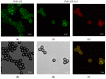
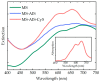
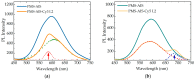
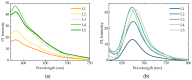
Here we report on the development and investigation of a novel multiplex assay model based on polymer microspheres (PMS) encoded with ternary AIS/ZnS quantum dots (QDs). The system was prepared via layer-by-layer deposition technique. Our studies of Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) between the QD-encoded microspheres and two different cyanine dyes have demonstrated that the QD photoluminescence (PL) quenching steadily increases with a decrease in the QD-dye distance. We have found that the sensitized dye PL intensity demonstrates a clear maximum at two double layers of polyelectrolytes between QDs and Dye molecules on the polymer microspheres. Time resolved PL measurements have shown that the PL lifetime decreases for the QDs and increases for the dyes due to FRET. The designed system makes it possible to record spectrally different bands of FRET-induced dye luminescence with different decay times and thereby allows for the multiplexing by wavelength and photoluminescence lifetimes of the dyes. We believe that PMS encoded with AIS/ZnS QDs have great potential for the development of new highly selective and sensitive sensor systems for multiplex analysis to detect cell lysates and body fluids' representative biomarkers.
Keywords: AgInS2; FRET; cyanine dyes; microspheres; sensing; ternary quantum dots; time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Ramasamy P., Kim N., Kang Y.-S., Ramirez O., Lee J.-S. Tunable, Bright, and Narrow-Band Luminescence from Colloidal Indium Phosphide Quantum Dots. Chem. Mater. 2017;29:6893–6899. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02204. - DOI
-
- Willard D.M., Carillo L.L., Jung J., Van Orden A. CdSe−ZnS Quantum Dots as Resonance Energy Transfer Donors in a Model Protein−Protein Binding Assay. Nano Lett. 2001;1:469–474. doi: 10.1021/nl015565n. - DOI
-
- Hyldahl M.G., Bailey S.T., Wittmershaus B.P. Photo-stability and performance of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in luminescent solar concentrators. Sol. Energy. 2009;83:566–573. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2008.10.001. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

