The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Immune Cells
- PMID: 33466553
- PMCID: PMC7824874
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11010060
The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Immune Cells
Abstract
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is the major intracellular and non-lysosomal protein degradation system. Thanks to its unique capacity of eliminating old, damaged, misfolded, and/or regulatory proteins in a highly specific manner, the UPS is virtually involved in almost all aspects of eukaryotic life. The critical importance of the UPS is particularly visible in immune cells which undergo a rapid and profound functional remodelling upon pathogen recognition. Innate and/or adaptive immune activation is indeed characterized by a number of substantial changes impacting various cellular processes including protein homeostasis, signal transduction, cell proliferation, and antigen processing which are all tightly regulated by the UPS. In this review, we summarize and discuss recent progress in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms by which the UPS contributes to the generation of an adequate immune response. In this regard, we also discuss the consequences of UPS dysfunction and its role in the pathogenesis of recently described immune disorders including cancer and auto-inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: autoinflammation; cancer; immunity; proteostasis; ubiquitin–proteasome system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
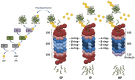
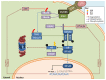
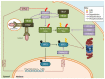

References
-
- Ciechanover A., Elias S., Heller H., Ferber S., Hershko A. Characterization of the heat-stable polypeptide of the ATP-dependent proteolytic system from reticulocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:7525–7528. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson K.D., Urban M.K., Haas A.L. Ubiquitin is the ATP-dependent proteolysis factor I of rabbit reticulocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:7529–7532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

