Functional Evaluation of a Rare Variant c.516G>C (p.Trp172Cys) in the GJB2 (Connexin 26) Gene Associated with Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss
- PMID: 33466560
- PMCID: PMC7824951
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11010061
Functional Evaluation of a Rare Variant c.516G>C (p.Trp172Cys) in the GJB2 (Connexin 26) Gene Associated with Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss
Abstract
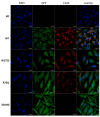
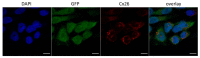
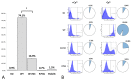
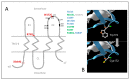
Mutations in the GJB2 gene encoding transmembrane protein connexin 26 (Cx26) are the most common cause for hearing loss worldwide. Cx26 plays a crucial role in the ionic and metabolic homeostasis in the inner ear, indispensable for normal hearing process. Different pathogenic mutations in the GJB2 gene can affect all stages of the Cx26 life cycle and result in nonsyndromic autosomal recessive (DFNB1) or dominant (DFNA3) deafness and syndromes associating hearing loss with skin disorders. This study aims to elucidate the functional consequences of a rare GJB2 variant c.516G>C (p.Trp172Cys) found with high frequency in deaf patients from indigenous populations of Southern Siberia (Russia). The substitution c.516G>C leads to the replacement of tryptophan at a conserved amino acid position 172 with cysteine (p.Trp172Cys) in the second extracellular loop of Cx26 protein. We analyzed the subcellular localization of mutant Cx26-p.Trp172Cys protein by immunocytochemistry and the hemichannels permeability by dye loading assay. The GJB2 knockout HeLa cell line has been generated using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing tool. Subsequently, the HeLa transgenic cell lines stably expressing different GJB2 variants (wild type and mutations associated with hearing loss) were established based on knockout cells and used for comparative functional analysis. The impaired trafficking of mutant Cx26-p.Trp172Cys protein to the plasma membrane and reduced hemichannels permeability support the pathogenic effect of the c.516G>C (p.Trp172Cys) variant and its association with nonsyndromic hearing loss. Our data contribute to a better understanding of the role of mutations in the second extracellular loop of Cx26 protein in pathogenesis of deafness.
Keywords: C (p.Trp172Cys); Connexin 26; GJB2; functional assay; gap junction channels; hearing loss; transgenic HeLa cell lines; variant c.516G>.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional Consequences of Pathogenic Variants of the GJB2 Gene (Cx26) Localized in Different Cx26 Domains.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 13;13(10):1521. doi: 10.3390/biom13101521. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unique Mutational Spectrum of the GJB2 Gene and its Pathogenic Contribution to Deafness in Tuvinians (Southern Siberia, Russia): A High Prevalence of Rare Variant c.516G>C (p.Trp172Cys).Genes (Basel). 2019 Jun 5;10(6):429. doi: 10.3390/genes10060429. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31195736 Free PMC article.
-
Three novel GJB2 (connexin 26) variants associated with autosomal dominant syndromic and nonsyndromic hearing loss.Am J Med Genet A. 2018 Apr;176(4):945-950. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38648. Am J Med Genet A. 2018. PMID: 29575629
-
Palmoplantar keratoderma with deafness phenotypic variability in a patient with an inherited GJB2 frameshift variant and novel missense variant.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Feb;9(2):e1574. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1574. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 33443819 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical phenotype and mutations in connexin 26 (DFNB1/GJB2), the most common cause of childhood hearing loss.Am J Med Genet. 1999 Sep 24;89(3):130-6. Am J Med Genet. 1999. PMID: 10704187 Review.
Cited by
-
A Chemical Chaperone Restores Connexin 26 Mutant Activity.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Jun 1;6(7):997-1005. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00056. eCollection 2023 Jul 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37470015 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Serum Inflammatory Markers in Infants Under 6 Months of Age with Non-Syndromic Moderate and Severe Hearing Loss Associated with GJB2 Gene Mutations.Med Sci Monit. 2023 Jan 3;29:e938165. doi: 10.12659/MSM.938165. Med Sci Monit. 2023. PMID: 36593740 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Consequences of Pathogenic Variants of the GJB2 Gene (Cx26) Localized in Different Cx26 Domains.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 13;13(10):1521. doi: 10.3390/biom13101521. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Phenotypes of GJB2 Missense Variants.Biology (Basel). 2023 Mar 27;12(4):505. doi: 10.3390/biology12040505. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexins, Innexins, and Pannexins: From Biology to Clinical Targets.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 25;11(2):155. doi: 10.3390/biom11020155. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33504027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Camp G., Smith R.J.H. Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage. [(accessed on 4 April 2019)]; Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org.
-
- Toriello H.V., Smith S.D. Hereditary Hearing Loss and Its Syndromes. 3rd ed. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2013. p. 756.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

