Mechanisms of the Morphological Plasticity Induced by Phytohormones and the Environment in Plants
- PMID: 33466729
- PMCID: PMC7828791
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020765
Mechanisms of the Morphological Plasticity Induced by Phytohormones and the Environment in Plants
Abstract
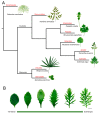
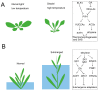
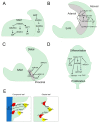
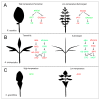
Plants adapt to environmental changes by regulating their development and growth. As an important interface between plants and their environment, leaf morphogenesis varies between species, populations, or even shows plasticity within individuals. Leaf growth is dependent on many environmental factors, such as light, temperature, and submergence. Phytohormones play key functions in leaf development and can act as molecular regulatory elements in response to environmental signals. In this review, we discuss the current knowledge on the effects of different environmental factors and phytohormone pathways on morphological plasticity and intend to summarize the advances in leaf development. In addition, we detail the molecular mechanisms of heterophylly, the representative of leaf plasticity, providing novel insights into phytohormones and the environmental adaptation in plants.
Keywords: environment; leaf; molecular mechanism; morphological plasticity; phytohormones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

