Neuronal Dopamine D3 Receptors: Translational Implications for Preclinical Research and CNS Disorders
- PMID: 33466844
- PMCID: PMC7830622
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11010104
Neuronal Dopamine D3 Receptors: Translational Implications for Preclinical Research and CNS Disorders
Abstract
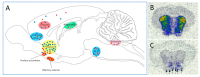
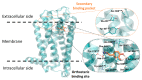
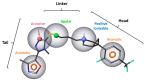
Dopamine (DA), as one of the major neurotransmitters in the central nervous system (CNS) and periphery, exerts its actions through five types of receptors which belong to two major subfamilies such as D1-like (i.e., D1 and D5 receptors) and D2-like (i.e., D2, D3 and D4) receptors. Dopamine D3 receptor (D3R) was cloned 30 years ago, and its distribution in the CNS and in the periphery, molecular structure, cellular signaling mechanisms have been largely explored. Involvement of D3Rs has been recognized in several CNS functions such as movement control, cognition, learning, reward, emotional regulation and social behavior. D3Rs have become a promising target of drug research and great efforts have been made to obtain high affinity ligands (selective agonists, partial agonists and antagonists) in order to elucidate D3R functions. There has been a strong drive behind the efforts to find drug-like compounds with high affinity and selectivity and various functionality for D3Rs in the hope that they would have potential treatment options in CNS diseases such as schizophrenia, drug abuse, Parkinson's disease, depression, and restless leg syndrome. In this review, we provide an overview and update of the major aspects of research related to D3Rs: distribution in the CNS and periphery, signaling and molecular properties, the status of ligands available for D3R research (agonists, antagonists and partial agonists), behavioral functions of D3Rs, the role in neural networks, and we provide a summary on how the D3R-related drug research has been translated to human therapy.
Keywords: D3 ligands; dopamine D3 functions; dopamine D3 receptor; localization; molecular structure; signalization; therapeutic indications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are employees of G. Richter Plc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the dopamine D3 receptor: an overview of drug design strategies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Jul;11(7):641-64. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1185413. Epub 2016 May 30. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27135354 Review.
-
Current drug treatments targeting dopamine D3 receptor.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Sep;165:164-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27343365 Review.
-
Identifying Medication Targets for Psychostimulant Addiction: Unraveling the Dopamine D3 Receptor Hypothesis.J Med Chem. 2015 Jul 23;58(14):5361-80. doi: 10.1021/jm501512b. Epub 2015 Mar 31. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25826710 Free PMC article.
-
Selective overexpression of dopamine D3 receptors in the striatum disrupts motivation but not cognition.Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Nov 15;76(10):823-31. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.11.023. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24387821 Free PMC article.
-
Chirality of Novel Bitopic Agonists Determines Unique Pharmacology at the Dopamine D3 Receptor.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 13;11(4):570. doi: 10.3390/biom11040570. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33924613 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of scan-time shortening on the 11C-PHNO binding potential to dopamine D3 receptor in humans and test-retest reliability.Ann Nucl Med. 2023 Apr;37(4):227-237. doi: 10.1007/s12149-022-01819-4. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Ann Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 36656501 Free PMC article.
-
Sex, Pramipexole and Tiagabine Affect Behavioral and Hormonal Response to Traumatic Stress in a Mouse Model of PTSD.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 30;12:691598. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.691598. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34276379 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D3 Receptor Plasticity in Parkinson's Disease and L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia.Biomedicines. 2021 Mar 19;9(3):314. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9030314. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33808538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G Protein-Dependent Activation of the PKA-Erk1/2 Pathway by the Striatal Dopamine D1/D3 Receptor Heteromer Involves Beta-Arrestin and the Tyrosine Phosphatase Shp-2.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 3;13(3):473. doi: 10.3390/biom13030473. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979407 Free PMC article.
-
D3 Receptor-Targeted Cariprazine: Insights from Lab to Bedside.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 23;25(11):5682. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115682. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amenta F., Ricci S.K., Tayebati R., Zaccheo D. The peripheral dopaminergic system: Morphological analysis, functional and clinical applications. Ital. J. Anat. Embryol. 2002;107:145–167. - PubMed
-
- Firsov M.L., Astakhova L.A. The role of dopamine in controlling retinal photoreceptor function in vertebrates. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2016;46:2016. doi: 10.1007/s11055-015-0210-9. - DOI
-
- Arreola R., Alvarez-Herrera S., Pérez-Sánchez G., Becerril-Villanueva E., Cruz-Fuentes C., Flores-Gutierrez O.E., Garcés-Alvarez M.E., de la Cruz-Aguilera D.L., Medina-Rivero E., Hurtado-Alvarado G., et al. Immunomodulatory effects mediated by dopamine. J. Immunol. Res. 2016;2016:3160486. doi: 10.1155/2016/3160486. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

