Beneficial Effects of Epigallocatechin-3- O-Gallate, Chlorogenic Acid, Resveratrol, and Curcumin on Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 33466849
- PMCID: PMC7829779
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26020415
Beneficial Effects of Epigallocatechin-3- O-Gallate, Chlorogenic Acid, Resveratrol, and Curcumin on Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
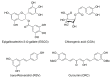
Many observational and clinical studies have shown that consumption of diets rich in plant polyphenols have beneficial effects on various diseases such as cancer, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). Animal and cellular studies have indicated that these polyphenolic compounds contribute to such effects. The representative polyphenols are epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate in tea, chlorogenic acids in coffee, resveratrol in wine, and curcumin in curry. The results of human studies have suggested the beneficial effects of consumption of these foods on NDDs including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, and cellular animal experiments have provided molecular basis to indicate contribution of these representative polyphenols to these effects. This article provides updated information on the effects of these foods and their polyphenols on NDDs with discussions on mechanistic aspects of their actions mainly based on the findings derived from basic experiments.
Keywords: AMPK; EGCG; NDD; NF-κB; ROS; chlorogenic acid; curcumin; polyphenols; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of microRNA modifications in anticancer effects of major polyphenols from green tea, coffee, wine, and curry.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(24):7148-7179. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2038540. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35289676
-
Anti-Cancer Effects of Green Tea Epigallocatchin-3-Gallate and Coffee Chlorogenic Acid.Molecules. 2020 Oct 5;25(19):4553. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194553. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33027981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Beneficial Effects of Principal Polyphenols from Green Tea, Coffee, Wine, and Curry on Obesity.Molecules. 2021 Jan 16;26(2):453. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020453. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33467101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Updated Review Summarizing the Anticancer Potential of Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Based Curcumin, Epigallocatechin Gallate, and Resveratrol Nanocarriers.Biopolymers. 2025 Jan;116(1):e23637. doi: 10.1002/bip.23637. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Biopolymers. 2025. PMID: 39417679 Review.
-
Modulation of Nrf2/ARE pathway by food polyphenols: a nutritional neuroprotective strategy for cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Oct;44(2):192-201. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8181-5. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21499987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Dairy-Fermented Products and Phenolic Compounds: Together or Apart.Molecules. 2023 Dec 14;28(24):8081. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248081. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Oral Green Tea Preparations in Skin Ailments: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies.Nutrients. 2022 Jul 30;14(15):3149. doi: 10.3390/nu14153149. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35956325 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors as Targets of Natural Compounds in Age-Related Diseases and Cancer: Potential Therapeutic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13882. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213882. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aerobic exercise combined with chlorogenic acid exerts neuroprotective effects and reverses cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease model mice (APP/PS1) via the SIRT1/ /PGC-1α/PPARγ signaling pathway.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 16;15:1269952. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1269952. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38046466 Free PMC article.
-
Artemisia scoparia and Metabolic Health: Untapped Potential of an Ancient Remedy for Modern Use.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 8;12:727061. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.727061. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35211087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tanabe H., Pervin M., Goto S., Isemura M., Nakamura Y. Beneficial Effects of Plant Polyphenols on Obesity. Obes. Control Ther. 2017;4:1–16. doi: 10.15226/2374-8354/4/3/00142. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

