Linear B-Cell Epitopes in Human Norovirus GII.4 Capsid Protein Elicit Blockade Antibodies
- PMID: 33466932
- PMCID: PMC7830539
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9010052
Linear B-Cell Epitopes in Human Norovirus GII.4 Capsid Protein Elicit Blockade Antibodies
Abstract
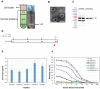
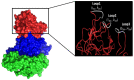
Human norovirus (HuNoV) is the leading cause of nonbacterial gastroenteritis worldwide with the GII.4 genotype accounting for over 80% of infections. The major capsid protein of GII.4 variants is evolving rapidly, resulting in new epidemic variants with altered antigenic potentials that must be considered for the development of an effective vaccine. In this study, we identify and characterize linear blockade B-cell epitopes in HuNoV GII.4. Five unique linear B-cell epitopes, namely P2A, P2B, P2C, P2D, and P2E, were predicted on the surface-exposed regions of the capsid protein. Evolving of the surface-exposed epitopes over time was found to correlate with the emergence of new GII.4 outbreak variants. Molecular dynamic simulation (MD) analysis and molecular docking revealed that amino acid substitutions in the putative epitopes P2B, P2C, and P2D could be associated with immune escape and the appearance of new GII.4 variants by affecting solvent accessibility and flexibility of the antigenic sites and histo-blood group antigens (HBAG) binding. Testing the synthetic peptides in wild-type mice, epitopes P2B (336-355), P2C (367-384), and P2D (390-400) were recognized as GII.4-specific linear blockade epitopes with the blocking rate of 68, 55 and 28%, respectively. Blocking rate was found to increase to 80% using the pooled serum of epitopes P2B and P2C. These data provide a strategy for expanding the broad blockade potential of vaccines for prevention of NoV infection.
Keywords: GII.4 genotype; linear blockade epitope; molecular dynamic simulation; norovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Particle conformation regulates antibody access to a conserved GII.4 norovirus blockade epitope.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):8826-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01192-14. Epub 2014 May 28. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24872579 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenetic mechanisms driving norovirus GII.4 antigenic variation.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(5):e1002705. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002705. Epub 2012 May 17. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22615565 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic mapping of a highly variable norovirus GII.4 blockade epitope: potential role in escape from human herd immunity.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(2):1214-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06189-11. Epub 2011 Nov 16. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22090110 Free PMC article.
-
GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape.Viruses. 2019 Feb 20;11(2):177. doi: 10.3390/v11020177. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30791623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antigenic Topology of Norovirus as Defined by B and T Cell Epitope Mapping: Implications for Universal Vaccines and Therapeutics.Viruses. 2019 May 10;11(5):432. doi: 10.3390/v11050432. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31083353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping Potential Vaccine Candidates Predicted by VaxiJen for Different Viral Pathogens between 2017-2021-A Scoping Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;10(11):1785. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111785. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366294 Free PMC article.
-
Linear epitopes on the capsid protein of norovirus commonly elicit high antibody response among past-infected individuals.Virol J. 2023 Jun 6;20(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02087-y. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37280660 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Immunogenic Linear B-Cell Epitopes in C. burnetii Outer Membrane Proteins Using Immunoinformatics Approaches Reveals Potential Targets of Persistent Infections.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 28;10(10):1250. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101250. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34684199 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Antigenic Peptides from Rocio Virus NS1 Protein for Immunodiagnostic Testing Using Immunoinformatics and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 12;23(14):7681. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147681. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887029 Free PMC article.
-
Immunodominant B-Cell Linear Epitope on the VP1 P Domain of a Feline Norovirus Cat Model.Pathogens. 2022 Jun 27;11(7):731. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11070731. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35889977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Havelaar A.H., Kirk M.D., Torgerson P.R., Gibb H.J., Hald T., Lake R.J., Praet N., Bellinger D.C., De Silva N.R., Gargouri N. World Health Organization Global estimates and regional comparisons of the burden of foodborne disease in 2010. PloS Med. 2015;12:e1001923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001923. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

