Biosensors Based on Isothermal DNA Amplification for Bacterial Detection in Food Safety and Environmental Monitoring
- PMID: 33467078
- PMCID: PMC7831002
- DOI: 10.3390/s21020602
Biosensors Based on Isothermal DNA Amplification for Bacterial Detection in Food Safety and Environmental Monitoring
Abstract
The easy and rapid spread of bacterial contamination and the risk it poses to human health makes evident the need for analytical methods alternative to conventional time-consuming laboratory-based techniques for bacterial detection. To tackle this demand, biosensors based on isothermal DNA amplification methods have emerged, which avoid the need for thermal cycling, thus facilitating their integration into small and low-cost devices for in situ monitoring. This review focuses on the breakthroughs made on biosensors based on isothermal amplification methods for the detection of bacteria in the field of food safety and environmental monitoring. Optical and electrochemical biosensors based on loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), rolling circle amplification (RCA), recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA), helicase dependent amplification (HDA), strand displacement amplification (SDA), and isothermal strand displacement polymerisation (ISDPR) are described, and an overview of their current advantages and limitations is provided. Although further efforts are required to harness the potential of these emerging analytical techniques, the coalescence of the different isothermal amplification techniques with the wide variety of biosensing detection strategies provides multiple possibilities for the efficient detection of bacteria far beyond the laboratory bench.
Keywords: bacteria; biosensor; environmental monitoring; food safety; helicase dependent amplification (HDA); isothermal DNA amplification; isothermal strand displacement polymerisation (ISDPR); loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP); recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA); rolling circle amplification (RCA); strand displacement amplification (SDA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

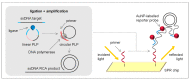


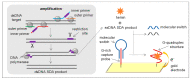
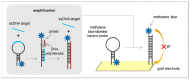
Similar articles
-
Miniaturized isothermal nucleic acid amplification, a review.Lab Chip. 2011 Apr 21;11(8):1420-30. doi: 10.1039/c0lc00666a. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Lab Chip. 2011. PMID: 21387067 Review.
-
Exponential Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acids and Assays for Proteins, Cells, Small Molecules, and Enzyme Activities: An EXPAR Example.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Sep 10;57(37):11856-11866. doi: 10.1002/anie.201712217. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29704305 Review.
-
Isothermal amplified detection of DNA and RNA.Mol Biosyst. 2014 May;10(5):970-1003. doi: 10.1039/c3mb70304e. Mol Biosyst. 2014. PMID: 24643211 Review.
-
A novel electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive and specific detection of DNA based on molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement and rolling circle amplification.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Dec 15;62:274-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.056. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 25022510
-
Nucleic acid amplification free biosensors for pathogen detection.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Apr 1;153:112049. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112049. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32056663 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid identification of Amanita citrinoannulata poisoning using colorimetric and real-time fluorescence and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) based on the nuclear ITS region.Food Chem (Oxf). 2022 Feb 4;4:100082. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100082. eCollection 2022 Jul 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35415685 Free PMC article.
-
Current Scenario of Pathogen Detection Techniques in Agro-Food Sector.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 4;12(7):489. doi: 10.3390/bios12070489. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic Factors and Recent Study on the Rapid Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC).Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan;67(1):16-26. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00985-8. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38153662 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Metallic Nanostructures-assisted Biosensors for Medical Diagnosis and Therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(11):930-951. doi: 10.2174/0115680266282489240109050225. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38243934 Review.
-
Design and 3D printing of an electrochemical sensor for Listeria monocytogenes detection based on loop mediated isothermal amplification.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 26;9(1):e12637. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12637. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36691544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO) [(accessed on 17 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety.
-
- Turner A., Karube I., Wilson G.S. Biosensors: Fundamentals and Applications. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1987.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

