A Numerical Study of Geometry's Impact on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Periodic Surface Structures
- PMID: 33467124
- PMCID: PMC7830026
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14020427
A Numerical Study of Geometry's Impact on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Periodic Surface Structures
Abstract
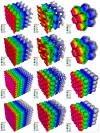
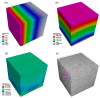
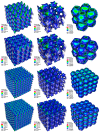
The paper focuses on thermal and mechanical analysis of Periodic Surface Structure (PSS). PSS is a continuous surface with a specific topology that is mathematically formulated by geometric factors. Cubic P-surface ("primitive"), D-surface ("diamond"), and G-surface ("gyroid") structures were simulated under load and heat transport using a numerical approach. We conducted our study by solving the stress and heat equations using the Finite Element Method (FEM). We achieved results using our software module, which generates PSS and simulates stress and temperature distribution. The stress model defined by dependence between stress and strain, gained from an experiment, and correlation of strain and displacement, gained from geometric conditions, was used in numerical experiments. The influence of geometric factors on the thermal and mechanical behavior of PSS was qualitatively determined. We showed decreasing effective stress values with an increased number of cells in the cubic domain for concerned PSS. It is important, because the increase in the number of cells does not increase the structure's volume.
Keywords: computer simulations; heat distribution; mechanical properties of advanced materials; modeling and simulation of material properties; numerical modeling; periodic surface structures; stress distribution; surface thickness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Finite-Element Modeling of the Hysteresis Behavior of Tetragonal and Rhombohedral Polydomain Ferroelectroelastic Structures.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;16(2):540. doi: 10.3390/ma16020540. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676277 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Hip Failure Load: In Vitro Study of 80 Femurs Using Three Imaging Methods and Finite Element Models-The European Fracture Study (EFFECT).Radiology. 2016 Sep;280(3):837-47. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016142796. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Radiology. 2016. PMID: 27077380
-
Fluid permeabilities of triply periodic minimal surfaces.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2005 Nov;72(5 Pt 2):056319. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.056319. Epub 2005 Nov 17. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2005. PMID: 16383757
-
Biomechanical Stress Analysis of Mandibular First Permanent Molar; Restored with Amalgam and Composite Resin: A Computerized Finite Element Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2010 Jan-Apr;3(1):5-14. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1047. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2010. PMID: 27625550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Mechanical Models for Cellular Media: Investigation on Material Characterization and Numerical Simulation.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 26;13(19):3283. doi: 10.3390/polym13193283. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Thermal Properties of a Prototype Insulation with a Gyroid Structure-Optimization of the Structure of a Cellular Composite Made Using SLS Printing Technology.Materials (Basel). 2022 Feb 12;15(4):1352. doi: 10.3390/ma15041352. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207893 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Computational Method in Designing a Unit Cell of Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffold: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2021 May 14;13(10):1584. doi: 10.3390/polym13101584. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical Properties of Porous Structures for Dental Implants: Experimental Study and Computational Homogenization.Materials (Basel). 2021 Aug 16;14(16):4592. doi: 10.3390/ma14164592. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34443120 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical Vibration Damping and Compression Properties of a Lattice Structure.Materials (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;14(6):1502. doi: 10.3390/ma14061502. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803878 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Die Land Length on the Maximum Extrusion Force and Dry Ice Pellets Density in Ram Extrusion Process.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;16(12):4281. doi: 10.3390/ma16124281. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37374466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fee C. 3D-printed porous bed structures. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2017;18:10–15. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2017.07.003. - DOI
-
- Maskery I., Aboulkhair N.T., Aremu A.O., Tuck C.J., Ashcroft I.A. Compressive failure modes and energy absorption in additively manufactured double gyroid lattices. Addit. Manuf. 2017;16:24–29. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2017.04.003. - DOI
-
- Sychov M., Lebedev L., Dyachenko S.V., Nefedova L.A. Mechanical properties of energy-absorbing structures with triply periodic minimal surface topology. Acta Astronaut. 2017;150:81–84. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2017.12.034. - DOI
-
- Khan K., Abu Al-Rub R. Time dependent response of architectured neovius foams. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017;126:106–119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.03.017. - DOI
-
- Monkova K., Monka P., Zetkova I., Hanzl P., Mandulak D. Three approaches to the gyroid structure modelling as a base of lightweight component produced by additive technology; Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (CMSAM 2017); Beijing, China. 22–23 October 2017; - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

