Influence of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Seed Cakes on Biochemical Values of Equine Plasma Subjected to Physical Exertion
- PMID: 33467154
- PMCID: PMC7829787
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11010210
Influence of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Seed Cakes on Biochemical Values of Equine Plasma Subjected to Physical Exertion
Abstract
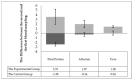
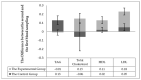
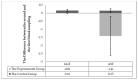
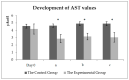
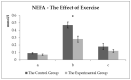
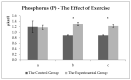
Veterinarians can recommend milk thistle for the treatment of equine liver disease and laminitis. Milk thistle seed cakes were fed in the range of normal feed doses in this study. The milk thistle seed cakes were fed (twice a day) to the experimental group of the horses (n = 5) and biochemical blood markers (TP, Albumin, ALT (alanine transaminase), AST (aspartate transaminase), ALP (alkaline phosphatase), GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase), Bilirubin, Cholesterol, HDL (high-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), TAG (triacylglycerol), BHB (beta-hydroxybutyric acid), NEFA (non-esterified fatty acids), creatine kinase, creatinine, Urea, GSH-Px (glutathione peroxidase), TAS (total antioxidant status), lactate, glucose, cortisol, Ca, Pi) were monitored. The control group of horses (n = 5), bred and trained in the same conditions, was used for comparison. The control group received the entire feed dose as accepted by the horses in the experimental group before the beginning of the experiment. The aim was to find out whether the preparation of milk thistle seed cakes could have positive effects on the health of the horses. All ten horses received one feeding form before the beginning of the experimental monitoring. All horses were exposed to heavy physical exercise (regular combined driving training) after 56 days of milk thistle seed cakes feeding (up to 400 g/day). Three blood samples were taken (before physical exercise; about 15 min and 60 min after physical exercise). Significant differences (p < 0.05) were detected in the values of AST, NEFA, cortisol and Pi in the experimental group. The exercise effect was detected in the values of albumin, lactate, cortisol, NEFA, and calcium. Our results suggest that the feeding of milk thistle seed cakes could have a positive effect on the health of the horses.
Keywords: biochemical parameters; horse nutrition; physical exercise; phytogenics; silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dose Effect of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Seed Cakes on the Digestibility of Nutrients, Flavonolignans and the Individual Components of the Silymarin Complex in Horses.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jun 5;11(6):1687. doi: 10.3390/ani11061687. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34198877 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Milk Thistle in Farm and Companion Animals: A Review.Planta Med. 2023 May;89(6):584-607. doi: 10.1055/a-1969-2440. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Planta Med. 2023. PMID: 36302565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Seed Cakes by Horses Subjected to Physical Exertion.J Equine Vet Sci. 2022 Jun;113:103937. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2022.103937. Epub 2022 Mar 19. J Equine Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35318098
-
Negative effect of feeding with high energy diets on testes and metabolic blood parameters of male Japanese quails, and positive role of milk thistle seed.Theriogenology. 2020 Mar 1;144:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.12.021. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Theriogenology. 2020. PMID: 31927417
-
The Milk Thistle Seed Cakes and Hempseed Cakes are Potential Feed for Poultry.Animals (Basel). 2020 Aug 10;10(8):1384. doi: 10.3390/ani10081384. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32785057 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Micelle silymarin supplementation to sows' diet from day 109 of gestation to entire lactation period enhances reproductive performance and affects serum hormones and metabolites.J Anim Sci. 2021 Dec 1;99(12):skab354. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab354. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34850001 Free PMC article.
-
Silybum marianum seed extract supplementation positively affects the body weight of weaned piglets by improving voluntary feed intake.J Anim Sci Technol. 2022 Jul;64(4):696-706. doi: 10.5187/jast.2022.e39. Epub 2022 Jul 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35969696 Free PMC article.
-
Dose Effect of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Seed Cakes on the Digestibility of Nutrients, Flavonolignans and the Individual Components of the Silymarin Complex in Horses.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jun 5;11(6):1687. doi: 10.3390/ani11061687. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34198877 Free PMC article.
-
Particle Size Distribution of Plasma Lipoproteins in Donkeys from Death Valley Compared to a Sampling of Horses.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 13;12(20):2746. doi: 10.3390/ani12202746. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290132 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Milk Thistle in Farm and Companion Animals: A Review.Planta Med. 2023 May;89(6):584-607. doi: 10.1055/a-1969-2440. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Planta Med. 2023. PMID: 36302565 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elghandour M.M.M.Y., Reddy P.R.K., Salem A.Z.M., Reddy P.P.R., Hyder I., Barbabosa-Pliego A. Plant Bioactives and Extracts as Feed Additives in Horse Nutrition. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018;69:66–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2018.06.004. - DOI
-
- Abenavoli L., Milic N. Silymarin for Liver Disease. In: Muriel P., editor. Liver Pathophysiology. 1st ed. Academic Press, Elsevier; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2017. pp. 621–631. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

