Molecular Epidemiological Analysis of the Origin and Transmission Dynamics of the HIV-1 CRF01_AE Sub-Epidemic in Bulgaria
- PMID: 33467166
- PMCID: PMC7829743
- DOI: 10.3390/v13010116
Molecular Epidemiological Analysis of the Origin and Transmission Dynamics of the HIV-1 CRF01_AE Sub-Epidemic in Bulgaria
Abstract
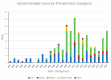
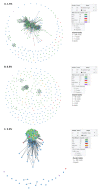
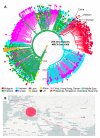
HIV-1 subtype CRF01_AE is the second most predominant strain in Bulgaria, yet little is known about the molecular epidemiology of its origin and transmissibility. We used a phylodynamics approach to better understand this sub-epidemic by analyzing 270 HIV-1 polymerase (pol) sequences collected from persons diagnosed with HIV/AIDS between 1995 and 2019. Using network analyses at a 1.5% genetic distance threshold (d), we found a large 154-member outbreak cluster composed mostly of persons who inject drugs (PWID) that were predominantly men. At d = 0.5%, which was used to identify more recent transmission, the large cluster dissociated into three clusters of 18, 12, and 7 members, respectively, five dyads, and 107 singletons. Phylogenetic analysis of the Bulgarian sequences with publicly available global sequences showed that CRF01_AE likely originated from multiple Asian countries, with Vietnam as the likely source of the outbreak cluster between 1988 and 1990. Our findings indicate that CRF01_AE was introduced into Bulgaria multiple times since 1988, and infections then rapidly spread among PWID locally with bridging to other risk groups and countries. CRF01_AE continues to spread in Bulgaria as evidenced by the more recent large clusters identified at d = 0.5%, highlighting the importance of public health prevention efforts in the PWID communities.
Keywords: HIV-1; circulating recombinant forms; drug resistance; molecular epidemiology; prevention; transmission clusters; transmission dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Hemelaar J., Elangovan R., Yun J., Dickson-Tetteh L., Fleminger I., Kirtley S., Williams B., Gouws-Williams E., Ghys P.D., Abimiku A.G., et al. Global and regional molecular epidemiology of HIV-1, 1990–2015: A systematic review, global survey, and trend analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019;19:143–155. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30647-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

