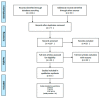
Sport Intervention Programs (SIPs) to Improve Health and Social Inclusion in People with Intellectual Disabilities: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33467372
- PMCID: PMC7739438
- DOI: 10.3390/jfmk4030057
Sport Intervention Programs (SIPs) to Improve Health and Social Inclusion in People with Intellectual Disabilities: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Inactivity is a major issue that causes physical and psychological health problems, especially in people with intellectual disability (ID). This review discusses the beneficial effects of sport intervention programs (SIPs) in people with ID, and aims to provide an overview of the scientific literature in order to identify the main factors influencing the participation of people with ID in SIPs. Twelve papers were analyzed and compared. The results show a large variety in examined SIPs, concerning participants' age and disability, intervention characteristics and context, as well as measures and findings. The main factors essential for people with ID partaking in SIPs appeared to be suitable places for the SIP development, adequate implementation of physical activity (PA) programs in school and extra-school contexts, education, and the training of teachers and instructors. The literature review highlights the relevance of using SIPs in order to improve physical and psychological health, as well as increase social inclusion in populations with ID. SIPs should be included in multifactor intervention programs. Nevertheless, the need is recognized for stakeholders to adopt specific practice and policy in promoting social inclusion in order to organize intervention strategies which are able to provide quality experiences in sport and physical activity for people with ID.
Keywords: equal opportunities; inclusion; intellectual disability; sport intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mastebroek M., Naaldenberg J., Lagro-Janssen A.L., Van Schrojenstein Lantman de Valk H. Health information exchange in general practice care for people with intellectual disabilities—A qualitative review of the literature. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014;35:1978–1987. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2014.04.029. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous