Optogenetic Stimulation of Prelimbic Pyramidal Neurons Maintains Fear Memories and Modulates Amygdala Pyramidal Neuron Transcriptome
- PMID: 33467450
- PMCID: PMC7830910
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020810
Optogenetic Stimulation of Prelimbic Pyramidal Neurons Maintains Fear Memories and Modulates Amygdala Pyramidal Neuron Transcriptome
Abstract
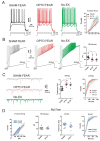
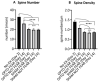
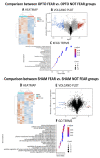
Fear extinction requires coordinated neural activity within the amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Any behavior has a transcriptomic signature that is modified by environmental experiences, and specific genes are involved in functional plasticity and synaptic wiring during fear extinction. Here, we investigated the effects of optogenetic manipulations of prelimbic (PrL) pyramidal neurons and amygdala gene expression to analyze the specific transcriptional pathways associated to adaptive and maladaptive fear extinction. To this aim, transgenic mice were (or not) fear-conditioned and during the extinction phase they received optogenetic (or sham) stimulations over photo-activable PrL pyramidal neurons. At the end of behavioral testing, electrophysiological (neural cellular excitability and Excitatory Post-Synaptic Currents) and morphological (spinogenesis) correlates were evaluated in the PrL pyramidal neurons. Furthermore, transcriptomic cell-specific RNA-analyses (differential gene expression profiling and functional enrichment analyses) were performed in amygdala pyramidal neurons. Our results show that the optogenetic activation of PrL pyramidal neurons in fear-conditioned mice induces fear extinction deficits, reflected in an increase of cellular excitability, excitatory neurotransmission, and spinogenesis of PrL pyramidal neurons, and associated to strong modifications of the transcriptome of amygdala pyramidal neurons. Understanding the electrophysiological, morphological, and transcriptomic architecture of fear extinction may facilitate the comprehension of fear-related disorders.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; differential gene expression; electrophysiological recordings; excitatory post-synaptic currents; fear conditioning; fear extinction; fear-related disorders; medial prefrontal cortex; spinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Trace Fear Conditioning Differentially Modulates Intrinsic Excitability of Medial Prefrontal Cortex-Basolateral Complex of Amygdala Projection Neurons in Infralimbic and Prelimbic Cortices.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 30;35(39):13511-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2329-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26424895 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic and transcriptomic features of cortical and amygdala pyramidal neurons predict inefficient fear extinction.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113066. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113066. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37656620
-
Synaptic Targeting of Double-Projecting Ventral CA1 Hippocampal Neurons to the Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Basal Amygdala.J Neurosci. 2017 May 10;37(19):4868-4882. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3579-16.2017. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28385873 Free PMC article.
-
Neural circuits and mechanisms involved in Pavlovian fear conditioning: a critical review.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30(2):188-202. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.06.005. Epub 2005 Aug 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006. PMID: 16120461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Out with the old and in with the new: Synaptic mechanisms of extinction in the amygdala.Brain Res. 2015 Sep 24;1621:231-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.010. Epub 2014 Oct 12. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25312830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β2-Adrenoceptors in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Excitatory Neurons Regulate Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 17;23(10):5578. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105578. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628393 Free PMC article.
-
Psychedelic control of neuroimmune interactions governing fear.Nature. 2025 May;641(8065):1276-1286. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08880-9. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40269152
-
How Fear Memory is Updated: From Reconsolidation to Extinction?Neurosci Bull. 2025 Jun;41(6):1054-1084. doi: 10.1007/s12264-025-01367-7. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Neurosci Bull. 2025. PMID: 40205305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebral cortex and hippocampus neural interaction during vagus nerve stimulation under in vivo large-scale imaging.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 2;17:1131063. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1131063. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36937685 Free PMC article.
-
The Three Musketeers in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex: Subregion-specific Structural and Functional Plasticity Underlying Fear Memory Stages.Exp Neurobiol. 2022 Aug 31;31(4):221-231. doi: 10.5607/en22012. Exp Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36050222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maren S., Fanselow M.S. The Amygdala and Fear Conditioning: Has the Nut Been Cracked? Neuron. 1996;16:237–240. - PubMed
-
- Davis M. The Role of the Amygdala in Conditioned and Unconditioned Fear and Anxiety. Amygdala. 2000;2:213–287.
-
- LeDoux J.E. Emotion Circuits in the Brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2000;23:155–184. - PubMed
-
- Fanselow M.S., Gale G.D. The Amygdala, Fear, and Memory. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003;985:125–134. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

