Alteration of Postural Balance in Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33467458
- PMCID: PMC7830486
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11010127
Alteration of Postural Balance in Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Balance problems are one of the most frequent symptoms in patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome (FMS). However, the extent and nature of this balance disorder are not known. The objective of this work was to determine the best evidence for the alteration of postural balance in patients with FMS and analyze differences with healthy controls. To meet this objective, a systematic review with meta-analysis was performed. A bibliographical search was carried out in PubMed Medline, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL and SciELO. Observational studies that assessed postural balance in patients with FMS compared to healthy subjects in baseline conditions, were selected. In a random-effect model, the pooled effect was calculated with the Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) and its 95% confidence interval (CI). Nineteen studies reporting data of 2347 participants (95% female) were included. FMS patients showed poor balance with a large effect on static (SMD = 1.578; 95% CI = 1.164, 1.992), dynamic (SMD = 0.946; 95% CI = 0.598, 1.294), functional balance (SMD = 1.138; 95% CI = 0.689, 1.588) and on balance confidence (SMD = 1.194; 95% CI = 0.914, 1.473). Analysis of the Sensory Organization Test showed large alteration of vestibular (SMD = 1.631; 95% CI = 0.467, 2.795) and visual scores (SMD = 1.317; 95% CI = 0.153, 2.481) compared to healthy controls. Patients with FMS showed worse scores for different measures of postural balance compared to healthy controls. Concretely, FMS patients appear to have poor vestibular and visual scores with a possible somatosensory dependence.
Keywords: central sensitization; chronic fatigue syndrome; fibromyalgia; meta-analysis; postural balance; sensory organization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
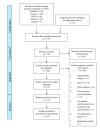



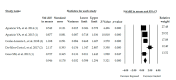


References
-
- Cerón Lorente L., García Ríos M.C., Navarro Ledesma S., Tapia Haro R.M., Casas Barragán A., Correa-Rodríguez M., Aguilar Ferrándiz M.E. Functional Status and Body Mass Index in Postmenopausal Women with Fibromyalgia: A Case–control Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019;16:4540. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16224540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Viseux F.J.F., Martins D.F., Villeneuve P., Charpentier P., de Sant’Anna e Silva L., Salgado A.S.I., Lemaire A. Effect of sensory stimulation applied under the great toe on postural ability in patients with fibromyalgia. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2020;37:172–179. doi: 10.1080/08990220.2020.1765767. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Di Tella M., Castelli L., Colonna F., Fusaro E., Torta R., Ardito R.B., Adenzato M. Theory of mind and emotional functioning in Fibromyalgia syndrome: An investigation of the relationship between social cognition and executive function. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0116542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

