Preliminary Evaluation of 3D Printed Chitosan/Pectin Constructs for Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 33467462
- PMCID: PMC7829944
- DOI: 10.3390/md19010036
Preliminary Evaluation of 3D Printed Chitosan/Pectin Constructs for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
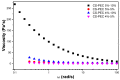
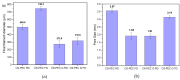
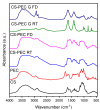
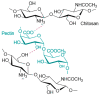
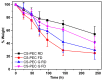
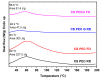
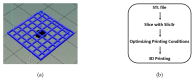
In the present study, chitosan (CS) and pectin (PEC) were utilized for the preparation of 3D printable inks through pneumatic extrusion for biomedical applications. CS is a polysaccharide with beneficial properties; however, its printing behavior is not satisfying, rendering the addition of a thickening agent necessary, i.e., PEC. The influence of PEC in the prepared inks was assessed through rheological measurements, altering the viscosity of the inks to be suitable for 3D printing. 3D printing conditions were optimized and the effect of different drying procedures, along with the presence or absence of a gelating agent on the CS-PEC printed scaffolds were assessed. The mean pore size along with the average filament diameter were measured through SEM micrographs. Interactions among the characteristic groups of the two polymers were evident through FTIR spectra. Swelling and hydrolysis measurements confirmed the influence of gelation and drying procedure on the subsequent behavior of the scaffolds. Ascribed to the beneficial pore size and swelling behavior, fibroblasts were able to survive upon exposure to the ungelated scaffolds.
Keywords: 3D printing; chitosan; hydrogels; pectin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Optimization of chitosan-gelatin-based 3D-printed scaffolds for tissue engineering and drug delivery applications.Int J Pharm. 2024 Dec 5;666:124776. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124776. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39343329
-
Bioinspired 3D printable pectin-nanocellulose ink formulations.Carbohydr Polym. 2019 Sep 15;220:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.026. Epub 2019 May 8. Carbohydr Polym. 2019. PMID: 31196530
-
A 3D printed chitosan-pectin hydrogel wound dressing for lidocaine hydrochloride delivery.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Nov;104:109873. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.109873. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 31500054
-
Chitosan hydrogels in 3D printing for biomedical applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 May 15;260:117768. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117768. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33712126 Review.
-
Composite Inks for Extrusion Printing of Biological and Biomedical Constructs.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021 Sep 13;7(9):4009-4026. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01158. Epub 2020 Nov 10. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 34510905 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Chitosan on Rheological, Mechanical, and Adhesive Properties of Pectin-Calcium Gel.Mar Drugs. 2023 Jun 25;21(7):375. doi: 10.3390/md21070375. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37504906 Free PMC article.
-
3D printed chitosan/polycaprolactone scaffold for lung tissue engineering: hope to be useful for COVID-19 studies.RSC Adv. 2021 May 28;11(32):19508-19520. doi: 10.1039/d1ra03410c. eCollection 2021 May 27. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479204 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 3D-Printed Dressings of Chitosan-Vanillin-Modified Chitosan Blends Loaded with Fluticasone Propionate for Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 18;14(9):1966. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091966. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145714 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterials / bioinks and extrusion bioprinting.Bioact Mater. 2023 Jun 27;28:511-536. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.06.006. eCollection 2023 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 37435177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atorvastatin liposomes in a 3D-printed polymer film: a repurposing approach for local treatment of oral candidiasis.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023 Nov;13(11):2847-2868. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01353-4. Epub 2023 May 15. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37184748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000;46:1–27. doi: 10.1016/S1381-5148(00)00038-9. - DOI
-
- Safdar R., Omar A.A., Arunagiri A., Regupathi I., Thanabalan M. Potential of Chitosan and its derivatives for controlled drug release applications—A review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019;49:642–659. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2018.10.020. - DOI
-
- Jayakumar R., Menon D., Manzoor K., Nair S.V., Tamura H. Biomedical applications of chitin and chitosan based nanomaterials—A short review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010;82:227–232. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.04.074. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

