Composition and Nutritional Value of Acid Oils and Fatty Acid Distillates Used in Animal Feeding
- PMID: 33467545
- PMCID: PMC7830271
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11010196
Composition and Nutritional Value of Acid Oils and Fatty Acid Distillates Used in Animal Feeding
Abstract
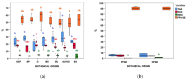
Acid oils (AO) and fatty acid distillates (FAD) are oil refining by-products rich in free fatty acids. The objective of this study is their characterization and the identification of their sources of variability so that they can be standardized to improve their use as feed ingredients. Samples (n=92) were collected from the Spanish market and the MIU value (sum of moisture, insoluble impurities, and unsaponifiable matter), lipid classes, fatty acid composition, and tocol content were analyzed. Their composition was highly variable even between batches from the same producer. As FAD originated from a distillation step, they showed higher free fatty acid amounts (82.5 vs 57.0 g/100 g, median values), whereas AO maintained higher proportions of moisture, polymers, tri-, di-, and monoacylglycerols. Overall, the MIU value was higher in AO (2.60-18.50 g/100 g in AO vs 0.63-10.44 g/100 g in FAD), with most of the contents of insoluble impurities being higher than those in the guidelines. Tocol and fatty acid composition were influenced by the crude oil's botanical origin. The calculated dietary energy values were, in general, higher for AO and decreased when a MIU correction factor was applied. The analytical control and standardization of these by-products is of the outmost importance to revalorize them as feed ingredients.
Keywords: MIU value; acid oils; animal feed; energy; fat by-products; fatty acid distillates; nutritional value; pig; poultry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Ghazani S.M., Marangoni A.G. Minor components in canola oil and effects of refining on these constituents: A review. JAOCS, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013;90:923–932. doi: 10.1007/s11746-013-2254-8. - DOI
-
- FEDIOL, The European Vegetable Oil and Protein Meal Industry Association—Refining of Edible Oils. [(accessed on 30 October 2020)]; Available online: www.fediol.eu/web/refining/1011306087/list1187970096/f1.html.
-
- Gibon V., De Greyt W., Kellens M. Palm oil refining. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007;109:315–335. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.200600307. - DOI
-
- FEDNA (Fundación Española para el Desarrollo de la Nutrición Animal) Tablas FEDNA de Composición y Valor Nutritivo de Alimentos para la Fabricación de Piensos Compuestos, 3rd ed.; Blas, C.; Mateos, G.G.; García-Rebollar, P. Eds; Madrid, Spain. [(accessed on 20 September 2020)];2010 Available online: http://www.fundacionfedna.org/ingredientes-para-piensos.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

