Effect of Linear and Nonlinear Pedagogy Physical Education Interventions on Children's Physical Activity: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial (SAMPLE-PE)
- PMID: 33467568
- PMCID: PMC7830495
- DOI: 10.3390/children8010049
Effect of Linear and Nonlinear Pedagogy Physical Education Interventions on Children's Physical Activity: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial (SAMPLE-PE)
Abstract
Background: School-based interventions are a key opportunity to improve children's physical activity (PA); however, there is lack of evidence about how pedagogical approaches to motor learning in physical education (PE) might affect PA in children. Therefore, this study aimed to assess how different pedagogical approaches in PE might affect children's PA.
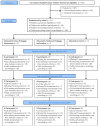
Methods: Participants (n = 360, 5-6 years) from 12 primary schools within the SAMPLE-PE randomized controlled trial were randomly allocated to either Linear Pedagogy (LP: n = 3) or Nonlinear Pedagogy (NP: n = 3) interventions, where schools received a 15-week PE intervention delivered by trained coaches, or to a control group (n = 6), where schools followed usual practice. ActiGraph GT9X accelerometers were used to assess PA metrics (moderate-to-vigorous PA, mean raw acceleration and lowest acceleration over the most active hour and half hour) over whole and segmented weeks at baseline, immediately post-intervention and 6 months follow-up. Intention to treat analysis employing multilevel modelling was used to assess intervention effects.
Results: LP and NP interventions did not significantly affect children's PA levels compared to the control group.
Conclusion: PE interventions based on LP and NP alone might not be effective in improving habitual PA in children.
Keywords: accelerometers; curriculum; movement competence; primary school; teaching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical activity promoting teaching practices and children's physical activity within physical education lessons underpinned by motor learning theory (SAMPLE-PE).PLoS One. 2022 Aug 1;17(8):e0272339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272339. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35913904 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Skill Acquisition Methods Fostering Physical Literacy in Early-Physical Education (SAMPLE-PE): Rationale and Study Protocol for a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial in 5-6-Year-Old Children From Deprived Areas of North West England.Front Psychol. 2020 Jun 17;11:1228. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01228. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32625143 Free PMC article.
-
Children's physical activity during a segmented school week: results from a quasi-experimental education outside the classroom intervention.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017 Jun 20;14(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12966-017-0534-7. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017. PMID: 28633656 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Physical Education-Based Physical Activity Interventions Among Elementary School Children.J Prim Prev. 2018 Jun;39(3):303-327. doi: 10.1007/s10935-018-0507-x. J Prim Prev. 2018. PMID: 29705883
-
The Behavioral Effects of Montessori Pedagogy on Children's Psychological Development and School Learning.Children (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;9(2):133. doi: 10.3390/children9020133. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
School-based promotion of physical literacy: a scoping review.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 8;12:1322075. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1322075. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38525332 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity promoting teaching practices and children's physical activity within physical education lessons underpinned by motor learning theory (SAMPLE-PE).PLoS One. 2022 Aug 1;17(8):e0272339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272339. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35913904 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of running experience and speed on local dynamic stability in running.Front Sports Act Living. 2025 Apr 3;7:1387934. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1387934. eCollection 2025. Front Sports Act Living. 2025. PMID: 40248211 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of linear and nonlinear pedagogy on motor skill performance: the moderating role of adaptability.Front Psychol. 2025 Mar 31;16:1540821. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1540821. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40230988 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Fundamental Movement Skills during Early Childhood: An Intervention Mapping Approach.Children (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;10(6):1004. doi: 10.3390/children10061004. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tarp J., Brønd J.C., Andersen L.B., Møller N.C., Froberg K., Grøntved A. Physical activity, Sedentary behavior, And long-term cardiovascular risk in young people: A review and discussion of methodology in prospective studies. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016;5:145–150. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2016.03.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donnelly J.E., Hillman C.H., Castelli D., Etnier J.L., Lee S., Tomporowski P., Lambourne K., Szabo-Reed A.N. Physical activity, fitness, cognitive function, and academic achievement in children: A systematic review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016;48:1197–1222. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000901. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous