Synergistic Effect of Abietic Acid with Oxacillin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
- PMID: 33467635
- PMCID: PMC7830589
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10010080
Synergistic Effect of Abietic Acid with Oxacillin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Abstract
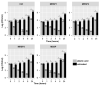
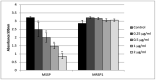
Resin acids are valued in traditional medicine for their antiseptic properties. Among these, abietic acid has been reported to be active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains. In veterinary healthcare, the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MRSP) strain is an important reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes including mecA. The incidence of MRSP has been increasing, and treatment options in veterinary medicine are partial. Here, we investigated the antimicrobial and antibiofilm properties of abietic acid against three MRSP and two methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MSSP) strains, isolated from diseased pet animals and human wound samples. Abietic acid showed a significant minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) value ranging from 32 to 64 μg/mL (MRSPs) and 8 μg/mL (MSSP). By checkerboard method we demonstrated that abietic acid increased oxacillin susceptibility of MRSP strains, thus showing a synergistic interaction with oxacillin. Abietic acid was also able to contrast the vitality of treated MSSP and MRSP1 biofilms at 20 μg/mL and 40 μg/mL, respectively. Finally, the compound moderately reduced mecA, mecR1 and mec1 gene expression. In conclusion, the results here reported demonstrate the antimicrobial activity of abietic acid against MRSP and support the use of this compound as a potential therapeutic agent to be used in combinatorial antibiotic therapy.
Keywords: Staphylococcus pseudintermedius; abietic acid; antimicrobial activity; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius; methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus pseudintermedius; synergistic interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Arciola C.R., Campoccia D., Gamberini S., Donati M.E., Pirini V., Visai L., Speziale P., Montanaro L. Antibiotic resistance in exopolysaccharide-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates from orthopaedic implant infections. Biomaterials. 2005;26:6530–6535. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.04.031. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

