Linking Gut Microbiome and Lipid Metabolism: Moving beyond Associations
- PMID: 33467644
- PMCID: PMC7830997
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11010055
Linking Gut Microbiome and Lipid Metabolism: Moving beyond Associations
Abstract
Various studies aiming to elucidate the role of the gut microbiome-metabolome co-axis in health and disease have primarily focused on water-soluble polar metabolites, whilst non-polar microbial lipids have received less attention. The concept of microbiota-dependent lipid biotransformation is over a century old. However, only recently, several studies have shown how microbial lipids alter intestinal and circulating lipid concentrations in the host, thus impacting human lipid homeostasis. There is emerging evidence that gut microbial communities play a particularly significant role in the regulation of host cholesterol and sphingolipid homeostasis. Here, we review and discuss recent research focusing on microbe-host-lipid co-metabolism. We also discuss the interplay of human gut microbiota and molecular lipids entering host systemic circulation, and its role in health and disease.
Keywords: gut; lipidomics; lipids; metabolomics; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
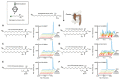
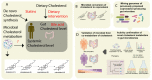
References
-
- Tran T.T., Postal B.G., Demignot S., Ribeiro A., Osinski C., Pais de Barros J.P., Blachnio-Zabielska A., Leturque A., Rousset M., Ferre P., et al. Short Term Palmitate Supply Impairs Intestinal Insulin Signaling via Ceramide Production. J. Biol. Chem. 2016;291:16328–16338. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.709626. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wei F., Lamichhane S., Orešič M., Hyötyläinen T. Lipidomes in health and disease: Analytical strategies and considerations. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019;120:115664. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.115664. - DOI
-
- VanHook A.M. Microbial metabolites shape lipid metabolism. Sci. Signal. 2020;13:eabc1552. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abc1552. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

