Method used to establish a large animal model of drug-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 33467911
- PMCID: PMC8024500
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370220981756
Method used to establish a large animal model of drug-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
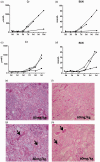
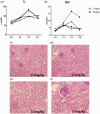
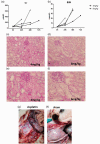
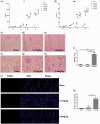
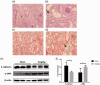
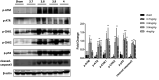
Acute kidney injury is a serious health hazard disease due to its complex etiology and lack of effective treatments, resulting in high medical costs and high mortality. At present, a large number of basic research studies on acute kidney injury have been carried out. However, acute kidney injury models established in rodents sometimes do not simulate the course of human disease well. Research in large animal models of acute kidney injury is relatively rare, and methods to build a mature model of acute kidney injury have failed. Because its kidney anatomy and morphology are very similar to those in humans, the mini pig is an ideal animal in which to model kidney disease. Nephrotoxic drug-induced acute kidney injury has a high incidence. In this study, we established models of acute kidney injury induced by two drugs (gentamicin and cisplatin). Finally, the model of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury was developed successfully, but we found the model of gentamycin-induced acute kidney injury was not reproducible. Compared to other models, these models better represent acute kidney injury caused by antibiotics and chemotherapeutic drugs and provide a basis for the study of new treatments for acute kidney injury in a large animal model.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; drug-induced model; mini pig.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
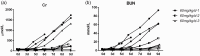
References
-
- Vicente-Vicente L, Casanova AG, Hernández-Sánchez MT, Pescador M, López-Hernández FJ, Morales AI. A systematic Meta-analysis on the efficacy of pre-clinically tested nephroprotectants at preventing aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 2017; 377:14–24 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

