Knockdown of circ-FANCA alleviates LPS-induced HK2 cell injury via targeting miR-93-5p/OXSR1 axis in septic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 33468219
- PMCID: PMC7816370
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-021-00625-8
Knockdown of circ-FANCA alleviates LPS-induced HK2 cell injury via targeting miR-93-5p/OXSR1 axis in septic acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is life-threatening disease with systemic inflammation and can lead to various diseases, including septic acute kidney injury (AKI). Recently, diverse circular RNAs (circRNAs) are considered to be involved in the development of this disease. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the role of circ-FANCA and the potential action mechanism in sepsis-induced AKI.
Methods: HK2 cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to establish septic AKI cell model. The expression of circ-FANCA, microRNA-93-5p (miR-93-5p) and oxidative stress responsive 1 (OXSR1) mRNA was determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell viability was assessed using cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Cell apoptosis and cell cycle distribution were measured by flow cytometry. The inflammatory response was monitored according to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The activities of oxidative indicators were examined using the corresponding kits. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay were applied to validate the interaction between miR-93-5p and circ-FANCA or OXSR1. Protein analysis was conducted through western blot.
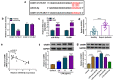
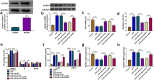
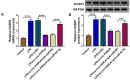
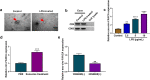
Results: Circ-FANCA was upregulated in septic AKI serum specimens and LPS-treated HK2 cells. Functionally, circ-FANCA knockdown facilitated cell proliferation and restrained apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in LPS-triggered HK2 cells. Further mechanism analysis revealed that miR-93-5p was a target of circ-FANCA and circ-FANCA modulated LPS-induced cell damage by targeting miR-93-5p. Meanwhile, miR-93-5p overexpression repressed LPS-treated HK2 cell injury by sponging OXSR1. Furthermore, circ-FANCA regulated OXSR1 expression by sponging miR-93-5p. Besides, exosome-derived circ-FANCA was upregulated in LPS-induced HK2 cells, which was downregulated by GW4869.
Conclusion: Circ-FANCA knockdown attenuated LPS-induced HK2 cell injury by regulating OXSR1 expression via targeting miR-93-5p.
Keywords: AKI; OXSR1; Sepsis; circ-FANCA; miR-93-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CIRC_0002131 CONTRIBUTES TO LPS-INDUCED APOPTOSIS, INFLAMMATION, AND OXIDATIVE INJURY IN HK-2 CELLS VIA INHIBITING THE BINDING BETWEEN MIR-942-5P AND OXSR1.Shock. 2023 Oct 1;60(4):517-524. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002197. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Shock. 2023. PMID: 37549022
-
CircNRIP1 KNOCKDOWN ALLEVIATES LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE-INDUCED HUMAN KIDNEY 2 CELL APOPTOSIS AND INFLAMMATION THROUGH miR-339-5p/OXSR1 PATHWAY.Shock. 2023 Mar 1;59(3):426-433. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002057. Epub 2023 Jan 8. Shock. 2023. PMID: 36609531
-
The novel biomarker circ_0020339 drives septic acute kidney injury by targeting miR-17-5p/IPMK axis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Feb;55(2):437-448. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03331-0. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 35986866
-
Circ_0114428 Regulates Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury by Targeting the miR-495-3p/CRBN Axis.Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44(4):1464-1477. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01432-z. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33830389
-
KNOCKDOWN OF CIRC_0114428 ALLEVIATES LPS-INDUCED HK2 CELL APOPTOSIS AND INFLAMMATION INJURY VIA TARGETING MIR-215-5P/TRAF6/NF-ΚB AXIS IN SEPTIC ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY.Shock. 2024 Apr 1;61(4):620-629. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002245. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Shock. 2024. PMID: 38010029
Cited by
-
Circular RNA_HIPK3-Targeting miR-93-5p Regulates KLF9 Expression Level to Control Acute Kidney Injury.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Feb 16;2023:1318817. doi: 10.1155/2023/1318817. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 36846202 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_UBE2D2 Attenuates the Progression of Septic Acute Kidney Injury in Rats by Targeting miR-370-3p/NR4A3 Axis.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 28;32(6):740-748. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2112.12038. Epub 2022 May 11. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35722711 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Inhibits circ_0074371-related Pathway to Alleviate Sepsis-induced Acute Kidney Injury.Biochem Genet. 2024 Jun;62(3):1779-1794. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10517-3. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37730967
-
Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Therapeutic Approach for Acute Kidney Injury.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 10;13:849891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849891. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35359949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircTLK1 modulates sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via enhancing PARP1/HMGB1 axis-mediated mitochondrial DNA damage by sponging miR-17-5p.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(17):8244-8260. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16738. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34410682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orlando V, La Manna MP, Goletti D, Palmieri F, Lo Presti E, Joosten SA, et al. Human CD4 T-cells With a Naive phenotype produce multiple cytokines during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and correlate with active disease. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1119. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

