Eosinopenia <100/μL as a marker of active COVID-19: An observational prospective study
- PMID: 33468435
- PMCID: PMC7792500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.12.005
Eosinopenia <100/μL as a marker of active COVID-19: An observational prospective study
Abstract
Objectives: To analyse the diagnostic performance of eosinopenia, alone or combined with polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) and/or lymphocytes, as a marker of active COVID-19 in patients hospitalized for suspicion of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Methods: A prospective observational study including patients hospitalized for suspicion of COVID-19 in a COVID unit was performed from 20th March to 5th April 2020, in Perpignan, France. Patients for which there was a doubt upon diagnosis, who were recently under oral corticosteroids, had myeloid malignancy or human immunodeficient virus infection were excluded. SARS-CoV-2 detection was performed using an RT-PCR assay, from nasopharyngeal swab specimens. Complete blood count were performed for all patients.
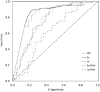
Results: One-hundred and twenty-one patient were included: 57 patients were diagnosed with COVID-19, 64 patients were not. Eosinophil count was lower in the COVID-19 group (median: 0/μL versus 70/μL, p < 0.0001). To diagnose COVID-19, eosinopenia had a sensitivity of 89.5% and a specificity of 78.1% while lymphopenia's were 73.7% and 62.5% respectively. Using area under curve (AUC) of receiving operating characteristics (ROC) curves, eosinophil's optimal cut-off level was 10/μL, sensitivity and specificity were 86%, and 79.7% respectively. Regarding the eosinophil/PMN ratio, the optimal cut-off level was 3.344, sensitivity and specificity were 87.7% and 73.4% respectively. The AUC of lymphocyte/PMN ratio was significantly lower than eosinophil/PMN ratio's (0.621 versus 0.846, p = 0.0003).
Conclusion: Eosinopenia - <10/μL - and eosinophil/PMN ratio are useful, low-cost, reproducible tools to help diagnose COVID-19, during an epidemic period, in a population of hospitalized patients admitted for suspicion of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Eosinopenia; Marker; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None of the authors mentioned above received any financial support or other benefits from commercial sources for the work reported on in the manuscript, or any other financial interests which could create a potential conflict of interest or the appearance of a conflict of interest with regard to the work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

