Boromycin Has Potent Anti- Toxoplasma and Anti- Cryptosporidium Activity
- PMID: 33468470
- PMCID: PMC8097477
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01278-20
Boromycin Has Potent Anti- Toxoplasma and Anti- Cryptosporidium Activity
Abstract
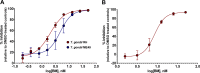
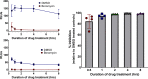
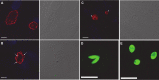
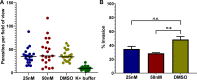
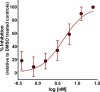
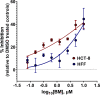
Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium parvum, members of the phylum Apicomplexa, are significant pathogens of both humans and animals worldwide for which new and effective therapeutics are needed. Here, we describe the activity of the antibiotic boromycin against Toxoplasma and Cryptosporidium Boromycin potently inhibited intracellular proliferation of both T. gondii and C. parvum at half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50) of 2.27 nM and 4.99 nM, respectively. Treatment of extracellular T. gondii tachyzoites with 25 nM boromycin for 30 min suppressed 84% of parasite growth, but T. gondii tachyzoite invasion into host cells was not affected by boromycin. Immunofluorescence of boromycin-treated T. gondii showed loss of morphologically intact parasites with randomly distributed surface antigens inside the parasitophorous vacuoles. Boromycin exhibited a high selectivity for the parasites over their host cells. These results suggest that boromycin is a promising new drug candidate for treating toxoplasmosis and cryptosporidiosis.
Keywords: Cryptosporidium parvum; Toxoplasma gondii; antiparasitic; boromycin; drug discovery.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Piekarski G. 1981. Behavioral alterations caused by parasitic infection in case of latent toxoplasma infection. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A 250:403–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

