Durable Effects of iGlarLixi Up to 52 Weeks in Type 2 Diabetes: The LixiLan-G Extension Study
- PMID: 33468520
- PMCID: PMC7896258
- DOI: 10.2337/dc20-2023
Durable Effects of iGlarLixi Up to 52 Weeks in Type 2 Diabetes: The LixiLan-G Extension Study
Abstract
Objective: In the LixiLan-G trial, switching to iGlarLixi, a once-daily titratable fixed-ratio combination of insulin glargine 100 units/mL and the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) lixisenatide, improved glucose control in type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with GLP-1 RAs over 26 weeks versus continuing prior GLP-1 RA. A prespecified, 26-week, single-arm extension of LixiLan-G aimed to determine the durability of iGlarLixi efficacy and safety over 52 weeks.
Research design and methods: Participants with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled by GLP-1 RAs (glycated hemoglobin [HbA1c] 7-9% [53-75 mmol/mol]) were initially randomized to switch to iGlarLixi or continue prior GLP-1 RA. Those randomized to iGlarLixi who completed the 26-week primary end point period could continue iGlarLixi open-label treatment over a 26-week extension to assess durability of efficacy and safety.
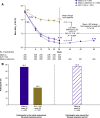
Results: Glycemic control achieved with iGlarLixi at week 26 (mean HbA1c 6.7% [50 mmol/mol]) was maintained at week 52 (mean HbA1c 6.7% [50 mmol/mol]; mean ± SD change from baseline at week 52: -1.0 ± 0.9% [11 ± 10 mmol/mol]). Proportions of participants reaching HbA1c <7% (53 mmol/mol) with iGlarLixi were similar at week 26 (62%) and 52 (64%), as were those reaching this target without documented symptomatic (<3.0 mmol/L) hypoglycemia (57% and 58%). Safety of iGlarLixi was similar at weeks 26 and 52, with low rates of documented symptomatic hypoglycemia and gastrointestinal events.
Conclusions: The efficacy and safety of iGlarLixi at the end of the 26-week randomized treatment period was maintained over the 26-week extension period in the LixiLan-G trial.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02787551.
© 2021 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency . Suliqua summary of product characteristics, 2019. Accessed 12 February 2020. Available from https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/suliqua-epar-...
-
- Sanofi . Soliqua US prescribing information, 2019. Accessed 12 February 2020. Available from https://products.sanofi.us/Soliqua100-33/Soliqua100-33.pdf
-
- Blonde L, Rosenstock J, Del Prato S, et al. . Switching to iGlarLixi versus continuing daily or weekly GLP-1 RA in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by GLP-1 RA and oral antihyperglycemic therapy: the LixiLan-G randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2019;42:2108–2116 - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association . 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43(Suppl. 1):S98–S110 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous