The Ugly Duckling Turned to Swan: A Change in Perception of Bystander-Activated Memory CD8 T Cells
- PMID: 33468558
- PMCID: PMC7839146
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000937
The Ugly Duckling Turned to Swan: A Change in Perception of Bystander-Activated Memory CD8 T Cells
Abstract
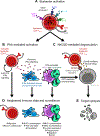
Memory T cells (Tmem) rapidly mount Ag-specific responses during pathogen reencounter. However, Tmem also respond to inflammatory cues in the absence of an activating TCR signal, a phenomenon termed bystander activation. Although bystander activation was first described over 20 years ago, the physiological relevance and the consequences of T cell bystander activation have only become more evident in recent years. In this review, we discuss the scenarios that trigger CD8 Tmem bystander activation including acute and chronic infections that are either systemic or localized, as well as evidence for bystander CD8 Tmem within tumors and following vaccination. We summarize the possible consequences of bystander activation for the T cell itself, the subsequent immune response, and the host. We highlight when T cell bystander activation appears to benefit or harm the host and briefly discuss our current knowledge gaps regarding regulatory signals that can control bystander activation.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
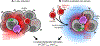
Similar articles
-
Significance of bystander T cell activation in microbial infection.Nat Immunol. 2022 Jan;23(1):13-22. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00985-3. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34354279 Review.
-
CXCR3 enables recruitment and site-specific bystander activation of memory CD8+ T cells.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 1;10(1):4987. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12980-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31676770 Free PMC article.
-
Bystander chronic infection negatively impacts development of CD8(+) T cell memory.Immunity. 2014 May 15;40(5):801-13. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.010. Immunity. 2014. PMID: 24837104 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of antigen-specific CD8 T cells results in minimal killing of bystander bacteria.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 1;171(11):6032-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.6032. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14634115
-
Bystander CD4+ T cells: crossroads between innate and adaptive immunity.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Aug;52(8):1255-1263. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-00486-7. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32859954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gestational influenza A virus infection elicits nonresolving vascular dysfunction and T-cell accumulation in the aorta of mice.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):H967-H977. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00646.2023. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39240256
-
Severe respiratory viral infections: T-cell functions diverging from immunity to inflammation.Trends Microbiol. 2023 Jun;31(6):644-656. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2022.12.008. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Trends Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36635162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T cells restrict immunity and pathology in distal tissue sites following a localized infection.Mucosal Immunol. 2024 Oct;17(5):923-938. doi: 10.1016/j.mucimm.2024.06.007. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Mucosal Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38908483 Free PMC article.
-
DAMP-ing IBD: Extinguish the Fire and Prevent Smoldering.Dig Dis Sci. 2025 Jan;70(1):49-73. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08523-5. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Dig Dis Sci. 2025. PMID: 38963463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The T cell immune response against SARS-CoV-2.Nat Immunol. 2022 Feb;23(2):186-193. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01122-w. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35105982 Review.
References
-
- Prlic M, Williams MA, and Bevan MJ 2007. Requirements for CD8 T-cell priming, memory generation and maintenance. Curr Opin Immunol 19: 315–319. - PubMed
-
- Tough DF, Borrow P, and Sprent J. 1996. Induction of bystander T cell proliferation by viruses and type I interferon in vivo. Science 272: 1947–1950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

