Discovery of a hidden transient state in all bromodomain families
- PMID: 33468647
- PMCID: PMC7848705
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2017427118
Discovery of a hidden transient state in all bromodomain families
Abstract
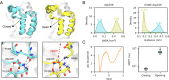
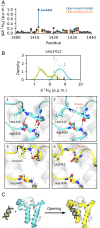
Bromodomains (BDs) are small protein modules that interact with acetylated marks in histones. These posttranslational modifications are pivotal to regulate gene expression, making BDs promising targets to treat several diseases. While the general structure of BDs is well known, their dynamical features and their interplay with other macromolecules are poorly understood, hampering the rational design of potent and selective inhibitors. Here, we combine extensive molecular dynamics simulations, Markov state modeling, and available structural data to reveal a transiently formed state that is conserved across all BD families. It involves the breaking of two backbone hydrogen bonds that anchor the ZA-loop with the αA helix, opening a cryptic pocket that partially occludes the one associated to histone binding. By analyzing more than 1,900 experimental structures, we unveil just two adopting the hidden state, explaining why it has been previously unnoticed and providing direct structural evidence for its existence. Our results suggest that this state is an allosteric regulatory switch for BDs, potentially related to a recently unveiled BD-DNA-binding mode.
Keywords: Markov models; allosteric effects; bromodomains; cryptic pockets; minor conformational states.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: K.M, J.G., and C.D.C. are employees and/or shareholders of Bayer AG.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In silico design and molecular basis for the selectivity of Olinone toward the first over the second bromodomain of BRD4.Proteins. 2020 Mar;88(3):414-430. doi: 10.1002/prot.25818. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Proteins. 2020. PMID: 31587361 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro, in cellulo and structural characterizations of the interaction between the integrase of Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus A/C and proteins of the BET family.Virology. 2019 Jun;532:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Virology. 2019. PMID: 31022666
-
Does bromodomain flexibility influence histone recognition?FEBS Lett. 2013 Jul 11;587(14):2158-63. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.05.032. Epub 2013 May 25. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23711371
-
Structure and acetyl-lysine recognition of the bromodomain.Oncogene. 2007 Aug 13;26(37):5521-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210618. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17694091 Review.
-
Co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor: the many faces of the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex.Biochem J. 2018 Dec 14;475(24):3921-3932. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170314. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30552170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A cryptic pocket in Ebola VP35 allosterically controls RNA binding.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 27;13(1):2269. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29927-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35477718 Free PMC article.
-
Folding-upon-binding pathways of an intrinsically disordered protein from a deep Markov state model.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 25:2023.07.21.550103. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.21.550103. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 6;121(6):e2313360121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313360121. PMID: 37546728 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Targeting protein conformations with small molecules to control protein complexes.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Dec;47(12):1023-1037. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.07.002. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35985943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystal structure of the BAZ2B TAM domain.Heliyon. 2022 Jul 6;8(7):e09873. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09873. eCollection 2022 Jul. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35865993 Free PMC article.
-
ARIP: A Tool for Precise Interatomic Contact Area and Volume Calculation in Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5176. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105176. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tokuriki N., Tawfik D. S., Protein dynamism and evolvability. Science 324, 203–207 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Campbell E., et al. , The role of protein dynamics in the evolution of new enzyme function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 12, 944–950 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Oleinikovas V., Saladino G., Cossins B. P., Gervasio F. L., Understanding cryptic pocket formation in protein targets by enhanced sampling simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 14257–14263 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

