Synthetic protein conjugate vaccines provide protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice
- PMID: 33468674
- PMCID: PMC7848748
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2013730118
Synthetic protein conjugate vaccines provide protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice
Abstract
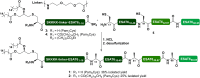
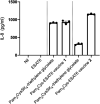
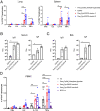
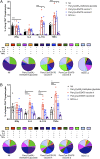
The global incidence of tuberculosis remains unacceptably high, with new preventative strategies needed to reduce the burden of disease. We describe here a method for the generation of synthetic self-adjuvanted protein vaccines and demonstrate application in vaccination against Mycobacterium tuberculosis Two vaccine constructs were designed, consisting of full-length ESAT6 protein fused to the TLR2-targeting adjuvants Pam2Cys-SK4 or Pam3Cys-SK4 These were produced by chemical synthesis using a peptide ligation strategy. The synthetic self-adjuvanting vaccines generated powerful local CD4+ T cell responses against ESAT6 and provided significant protection in the lungs from virulent M. tuberculosis aerosol challenge when administered to the pulmonary mucosa of mice. The flexible synthetic platform we describe, which allows incorporation of adjuvants to multiantigenic vaccines, represents a general approach that can be applied to rapidly assess vaccination strategies in preclinical models for a range of diseases, including against novel pandemic pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: chemical protein synthesis; mucosal vaccination; peptide ligation; self-adjuvanting; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

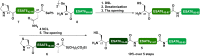

References
-
- WHO , Global Tuberculosis Report 2019 (World Health Organization, 2019). https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa.... Accessed 24 December 2020.
-
- Pai M., et al. , Tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2, 16076 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Andersen P., Doherty T. M., The success and failure of BCG—implications for a novel tuberculosis vaccine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3, 656–662 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Foged C., Subunit vaccines of the future: The need for safe, customized and optimized particulate delivery systems. Ther. Deliv. 2, 1057–1077 (2011). - PubMed
-
- McDonald D. M., et al. , Synthesis of a self-adjuvanting MUC1 vaccine via diselenide-selenoester ligation-deselenization. ACS Chem. Biol. 13, 3279–3285 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

