Crystal structure of steroid reductase SRD5A reveals conserved steroid reduction mechanism
- PMID: 33469028
- PMCID: PMC7815742
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20675-2
Crystal structure of steroid reductase SRD5A reveals conserved steroid reduction mechanism
Abstract
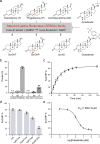
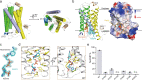
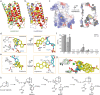
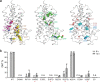
Steroid hormones are essential in stress response, immune system regulation, and reproduction in mammals. Steroids with 3-oxo-Δ4 structure, such as testosterone or progesterone, are catalyzed by steroid 5α-reductases (SRD5As) to generate their corresponding 3-oxo-5α steroids, which are essential for multiple physiological and pathological processes. SRD5A2 is already a target of clinically relevant drugs. However, the detailed mechanism of SRD5A-mediated reduction remains elusive. Here we report the crystal structure of PbSRD5A from Proteobacteria bacterium, a homolog of both SRD5A1 and SRD5A2, in complex with the cofactor NADPH at 2.0 Å resolution. PbSRD5A exists as a monomer comprised of seven transmembrane segments (TMs). The TM1-4 enclose a hydrophobic substrate binding cavity, whereas TM5-7 coordinate cofactor NADPH through extensive hydrogen bonds network. Homology-based structural models of HsSRD5A1 and -2, together with biochemical characterization, define the substrate binding pocket of SRD5As, explain the properties of disease-related mutants and provide an important framework for further understanding of the mechanism of NADPH mediated steroids 3-oxo-Δ4 reduction. Based on these analyses, the design of therapeutic molecules targeting SRD5As with improved specificity and therapeutic efficacy would be possible.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Approach1es for evolutionary, biochemical, and structural analysis of bacterial steroid 5α-reductases.Methods Enzymol. 2023;689:237-261. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2023.04.006. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Methods Enzymol. 2023. PMID: 37802572
-
Structure of human steroid 5α-reductase 2 with the anti-androgen drug finasteride.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 27;11(1):5430. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19249-z. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33110062 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of human liver Delta4-3-ketosteroid 5beta-reductase (AKR1D1) and implications for substrate binding and catalysis.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 13;283(24):16830-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801778200. Epub 2008 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18407998 Free PMC article.
-
The role of 5alpha-reduction in steroid hormone physiology.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2001;13(7-8):673-8. doi: 10.1071/rd01074. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2001. PMID: 11999320 Review.
-
Steroid metabolism in the mammalian brain: 5alpha-reduction and aromatization.Brain Res Bull. 1997;44(4):365-75. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(97)00216-5. Brain Res Bull. 1997. PMID: 9370201 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for recognition of N-formyl peptides as pathogen-associated molecular patterns.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 5;13(1):5232. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32822-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36064945 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights of the elongation factor EF-Tu complexes in protein translation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Commun Biol. 2022 Oct 3;5(1):1052. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04019-y. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36192483 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Two Known SRD5A2 Gene Variants in Mexican Patients With Disorder of Sexual Development.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 27;12:794476. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.794476. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35154247 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-receptor regulation of 11-oxyandrogens differs between normal and cancerous endometrium and across endometrial cancer grades and molecular subtypes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 14;15:1404804. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1404804. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39205690 Free PMC article.
-
Active DHEA uptake in the prostate gland correlates with aggressive prostate cancer.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 15;133(24):e171199. doi: 10.1172/JCI171199. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 38099500 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

